Introduction to Data Storage
Do you want to know the Three Types of Data Storage?
You have come to the right place.
In this comprehensive guide, I’ll explore the main three types of data storage and provide you with the insights you need to choose the right solution for your needs. I’ll walk you through each type, providing valuable insights to help you make informed decisions tailored to your needs. Today you will understand more about data storage and why it is important for you.
Table of Contents
Overview of the Three Types of Data Storage
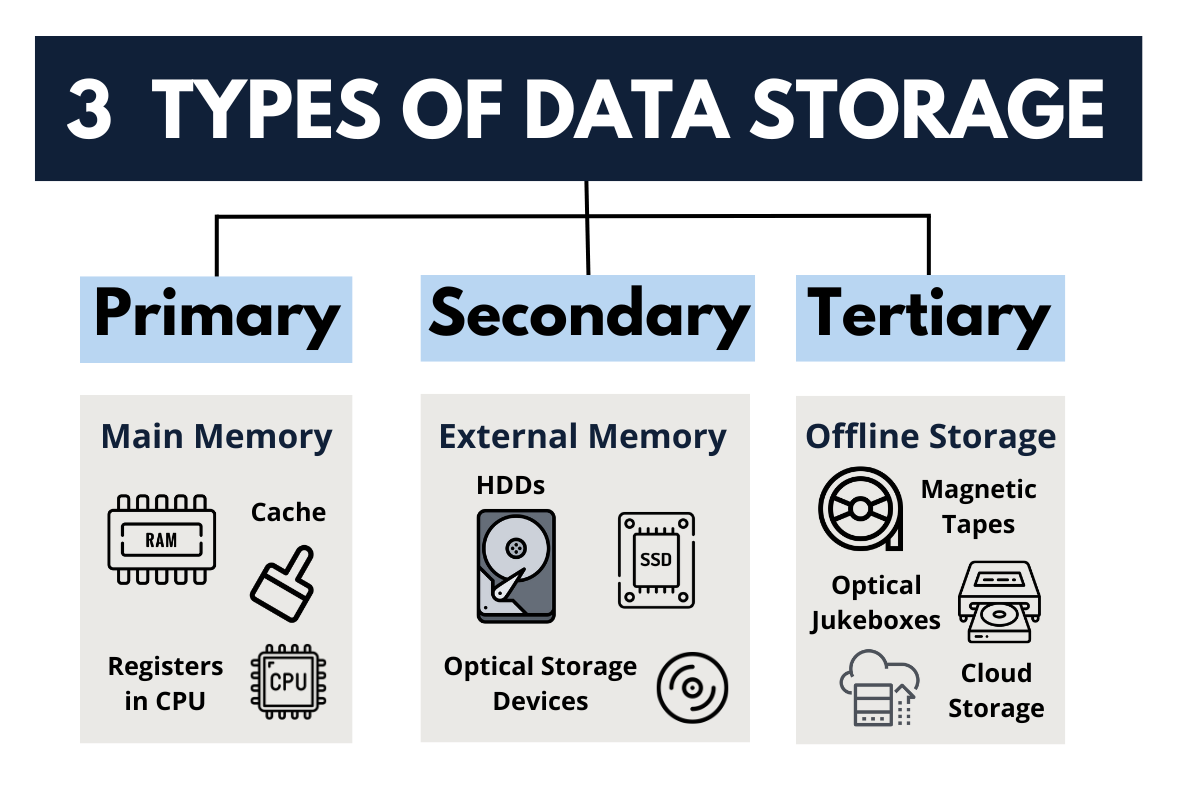
These are the three types of Data Storage, in a broad way:
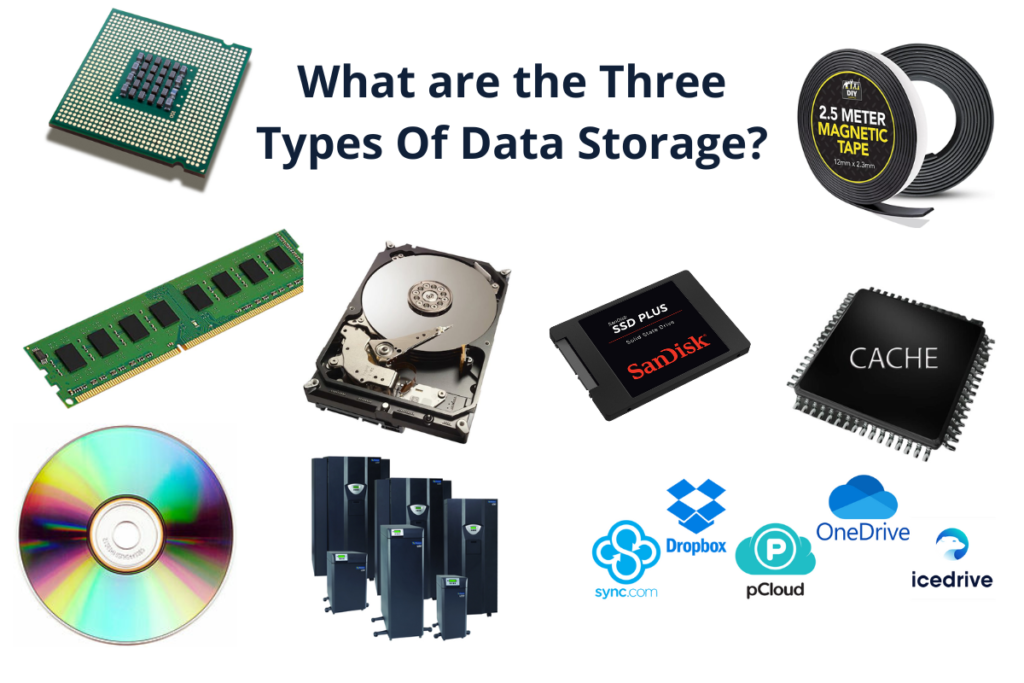
- primary storage or main memory (includes RAM, Cache Memory and Registers in CPU)
- secondary storage or external memory (includes HDDs, SSDs and Optical Storage Devices)
- tertiary storage or offline storage (includes Magnetic Tapes, Otical Junkboxes and Cloud Storage)
Each type serves a specific purpose and has its own unique characteristics. Let’s dive into the details of each:
Primary Storage (Main Memory) Explained
Primary storage, also known as primary memory or main memory, is the component of a computer system that stores data and instructions that are actively being used by the CPU (Central Processing Unit) during program execution. It is the fastest form of storage in a computer and is directly accessible by the CPU.
Primary storage is essential for the smooth operation of a computer system. It enables the processor to quickly access the data and instructions it needs to perform tasks.
Primary storage retains data temporarily and while the computer is powered on. When the computer is turned off, the data stored in primary storage is lost. Its primary function is to provide the CPU with quick access to the information it needs to perform tasks efficiently.
In essence, primary storage acts as the workspace for the computer, holding the data and instructions needed to be immediatly processed.
Types of Primary Storage
These are the main components of primary data storage are RAM (Random Access Memory), Cache Memory and Registers.
RAM (Random Access Memory)
RAM is the primary working memory of a computer system. It’s used to store data and instructions that the processor needs to access quickly.

Cache Memory
Cache memory is a high-speed storage located close to the processor, which helps to bridge the performance gap between the processor and main memory. Unlike RAM, cache memory is smaller but much faster, which facilitates rapid access to essential data.
Registers
Registers are high-speed storage locations within the processor itself, used to hold data and instructions for immediate use. They are the fastest form of memory in a computer system, offering nearly instantaneous access to data and instructions.
Secondary Storage (External Memory) Explained
Secondary storage, often referred to as external memory, is a type of non-volatile storage that retains large volumes of data even when the computer is powered off.
Unlike primary storage, which provides fast access to data and instructions for immediate processing by the CPU, secondary storage serves as a long-term repository for storing large volumes of data that do not need to be accessed frequently.
Secondary storage devices typically offer larger storage capacities and lower cost-per-byte compared to primary storage, making them suitable for storing files, applications, and operating systems over extended periods.
NAS (Network-Attached Storage) is an example of secondary storage. If you want to know what are the best NAS for Plex, please click on that link.
Types of Secondary Storage
The main types of external memory are Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), Solid-State Drives (SSDs) and Optical Storage Devices.
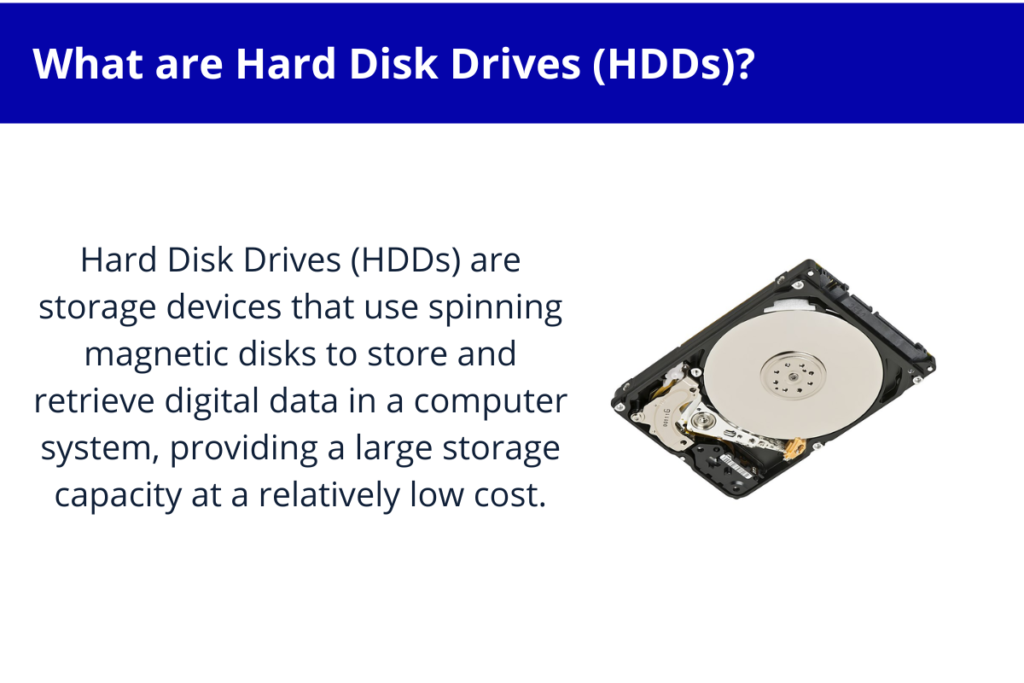
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
HDDs are the most common type of secondary storage.
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) are storage devices comprised of one or more spinning magnetic disks, also known as platters, coated with a magnetic material. These platters are paired with magnetic read/write heads that move rapidly over their surfaces to read and write data.
Data is stored on the platters in the form of magnetized regions, which can be accessed sequentially or randomly depending on the needs of the system.
HDDs typically offer large storage capacities and are commonly used for long-term data storage in computers, servers, and other electronic devices.
Solid-State Drives (SSDs)
Solid-State Drives (SSDs) are a newer type of secondary storage that use flash memory to store data. They are faster and more energy-efficient than HDDs, but also more expensive.
Unlike conventional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), which store data magnetically, SSDs store data electronically and they are completely mechanical. SSDs provide higher read and write rates due to their lack of moving parts, which enhances system responsiveness and performance. SSDs are also more resilient to physical shock and vibration, which increases their dependability and durability when used in portable electronics like laptops and tablets. Although SSDs usually have lower storage capacity than HDDs, improvements in flash memory technology have resulted in lower costs and higher storage densities, which has made SSDs a more and more popular option.
Optical Storage Devices
Optical Storage Devices utilize laser technology to read and write digital data into optical discs. It uses circular discs made of plastic or glass coated with a reflective layer.
When data is written into the disc, the laser burns tiny marks into the reflective layer, representing binary data. To read the data, a laser is directed into the surface of the disc, and the reflected light is detected by a sensor, allowing the data to be retrieved. Optical storage devices offer advantages such as portability, durability, and resistance to magnetic interference. They are commonly used for distributing software, music, movies, and archival data storage.
While optical discs have become less prevalent with the rise of high-capacity solid-state and cloud storage solutions, they remain a viable option for data archiving and distribution in certain industries and applications.
Tertiary Storage (Offline Storage) Explained
Tertiary storage, also known as offline storage or archival storage, is used for long-term data storage and backup. It is essential for long-term data preservation and disaster recovery, because it provides a reliable and cost-effective way to store large amounts of data that are not to be accessed frequently.
In contrast to primary and secondary storage, which give priority to speed and accessibility, tertiary storage gives more weight to longevity and cost-effectiveness. Tertiary storage alternatives are used by businesses and people looking for dependable, scalable, and affordable long-term storage solutions.
It’s the slowest and least accessible type of storage, but it offers the highest capacity and the most cost-effective solution for archiving data.
Types of Tertiary Storage
The main types of offline storage are magnetic tapes, optical jukeboxes and cloud storage:
Magnetic Tapes
Magnetic tapes are a traditional form of tertiary storage, often used for large-scale data backup and archiving.
Magnetic Tapes utilize magnetic technology to record and retrieve digital information. They consist of a long, narrow strip of tape coated with a magnetic material, onto which data is magnetically encoded in a sequential manner. Magnetic tapes offer high storage capacities and are often used for archival purposes due to their low cost-per-byte and longevity. Data is accessed by a tape drive, which reads and writes data as the tape moves past read/write heads. While magnetic tapes may have slower access times compared to other storage technologies, they still remain a popular choice for long-term data backup and archival.

Optical Jukeboxes
Optical jukeboxes are storage systems that automate the organization and retrieval of Optical Storage Devices., such as CDs, DVDs, or Blu-ray discs. They typically consist of mechanisms that can store and retrieve multiple discs from a library of media, like a jukebox for digital data. Optical jukeboxes are commonly used in environments where large volumes of data need to be stored and accessed efficiently, such as data centers or archival facilities. They offer scalability and ease of management, allowing you to expand your storage capacity by just adding additional discs when you need it. Additionally, optical jukeboxes often include features such as redundancy and data integrity checks to ensure the reliability and integrity of stored data over time.
Cloud Storage
Cloud storage is a modern form of tertiary storage, where data is stored on remote servers and accessed over the internet from anywhere with an internet connection.
This takes away the need for physical storage devices, such as hard drives or USBs, and enables you to access your data from various devices, including computers, smartphones, and tablets. Cloud storage services typically offer scalable storage options, allowing you to increase or decrease your storage capacity as needed, and often include features like data redundancy and encryption to ensure data availability and security. Additionally, cloud storage solutions may offer collaboration features that allow you and other people to access and edit shared files simultaneously.
This is why cloud storage private use has increased a lot in the last years. You can know here how many people use cloud storage.
Overall, cloud storage provides you with flexibility, accessibility, and peace of mind regarding data security and availability.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Data Storage Solution
When selecting a data storage solution, you must consider some factors like:
- Storage Capacity: Determine the amount of data you need to store and choose a solution that can accommodate your current and future needs.
- Performance Requirements: Consider the speed and accessibility requirements of your data. Primary storage is best for frequently accessed data, while secondary and tertiary storage are more suitable for less frequently accessed data.
- Cost: Evaluate the overall cost of the storage solution, including the initial investment, ongoing maintenance, and potential upgrade or replacement costs.
- Reliability and Durability: Ensure that the storage solution you choose is reliable and can withstand the expected usage and environmental conditions.
- Compatibility and Integration: Make sure the storage solution is compatible with your existing hardware and software, and can integrate seamlessly with your overall IT infrastructure.
- Data Security and Backup: Implement appropriate data security measures, such as encryption and backup strategies, to protect your valuable information. You can learn here how to protect your cloud storage.
Choosing the Right Type of Data Storage for Your Needs
When it comes to choosing the right type of data storage, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. The choice will depend on your specific needs, such as the amount of data you need to store, the frequency of access, the performance requirements, and the budget you have available.
However, certain forms of data storage may be more suitable for your needs than others, depending on the specifications you have. Here’s a guide to help you select between the three types of data storage based on the main feature you require.
High Storage Capacity
When you have a large volume of data to store, opt for storage solutions like Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) or Cloud Storage, known for their expansive storage capacities and scalability to accommodate vast amounts of data. Cloud Storage Services like Sync.com, Dropbox or pCloud offer safe storage services for a fair price.
Quick Access to Data
If you prioritize Swift Data Retrieval, consider Solid-State Drives (SSDs) for their rapid read and write speeds, ensuring quick access and manipulation of data compared to traditional HDDs.
Data Safety and Security
When safeguarding your data is essential, opt for storage options equipped with robust security features, such as encryption and redundancy. Cloud Storage and RAID configurations with multiple HDDs are ideal choices to ensuring the safety and integrity of your data.
Long-Term maintenance
For long-term data storage with minimal upkeep, explore storage solutions like Magnetic Tapes or Cloud Storage, which offer reliable data retention for long-term storage without the need for frequent maintenance.
Budget-Friendly Option
If cost is a priority, consider Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) for their high storage capacities at a lower cost per gigabyte. Alternatively, Cloud Storage services offer competitive pricing plans, making them an affordable option for storing large volumes of data in the cloud. Services like Terabox offer 1 TB of storage for free, but you would like to evaluate the safety of the service before storing your data there.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Each of the Three Types of Data Storage
To help you make an informed decision, let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of each type of data storage:
Primary Storage
Advantages
- Fastest access time
- Directly accessible by the processor
- Crucial for running applications and processes
Disadvantages
- Volatile (data is lost when power is turned off)
- Limited capacity
- More expensive per unit of storage
Secondary Storage
Advantages
- Large storage capacity
- Non-volatile (data is retained even when power is turned off)
- Relatively low cost per unit of storage
Disadvantages
- Slower access time compared to primary storage
- Susceptible to physical damage (e.g., mechanical failure in HDDs)
Tertiary Storage
Advantages
- Massive storage capacity
- Extremely low cost per unit of storage
- Reliable and durable for long-term data preservation
Disadvantages
- Slowest access time
- Limited direct accessibility (often requires manual intervention)
- Potential compatibility issues with older storage formats

Conclusion: What Are the Three Types of Data Storage?
In conclusion, the three main types of data storage are Main Memory, External Memory, and Offline Storage. Each type serves a specific purpose and has its own unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.
When choosing a data storage solution, it’s important to carefully evaluate your needs and select the right combination of storage types to meet your requirements. By understanding the differences between primary, secondary, and tertiary storage, you can make an informed decision and ensure that your data is stored securely, efficiently, and cost-effectively.
Please share this blog post with people you think will find this useful. Help them make informed decision about the three types of data storage.
If you need more help, you can send a message through my contact page. I’ll be happy to help you 🙂