Trying to know what are AI agents? You’re not alone.
AI agents are software programs with artificial intelligence that make decisions, learn from data, and interact with their environment—think Alexa or self-driving cars.
This post will show you what are AI agents and how these smart programs are reshaping our future. Get ready to see the world differently!
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- AI agents are smart AI programs that make decisions, learn over time, and act on their own. Examples include Alexa and self-driving cars.
- They work by sensing their environment, deciding the best action based on what they know, and then acting using parts like sensors and actuators.
- AI agents come in several types like reflex agents, goal-based agents, utility-based agents, learning agents which serve different purposes.
- They have many uses from driving cars without a person to helping with customer service tasks automatically.
- While AI agents can make things more efficient and save time, it’s important to watch out for risks like making biased choices or raising ethical issues.
What are AI agents?
AI agents are intelligent entities that can perceive their environment and take actions to achieve specific goals. They possess autonomy, continuous learning capabilities, reactivity to changes in their surroundings, and the ability to be proactive in decision-making.
What are AI Agents Characteristics?
AI agents are smart AI machines that make their own choices and learn as they go. They notice changes, think about what to do, and then do it to meet their goals. Here’s how:
- Autonomy means they work on their own without your help. Like a robot vacuum that cleans your room by itself.
- Continuous Learning is when they get smarter from experiences. Imagine playing a video game – the more you play, the better you get. That’s what AI agents do; they use machine learning to improve.
- Reactivity helps them notice and react to changes fast. If there’s a new obstacle, like a chair in the way of our robot vacuum, it will go around it without you having to move it.
- Proactivity is about taking action by themselves to achieve their goals. Think of a virtual assistant reminding you of your friend’s birthday so you can buy a gift before the date.
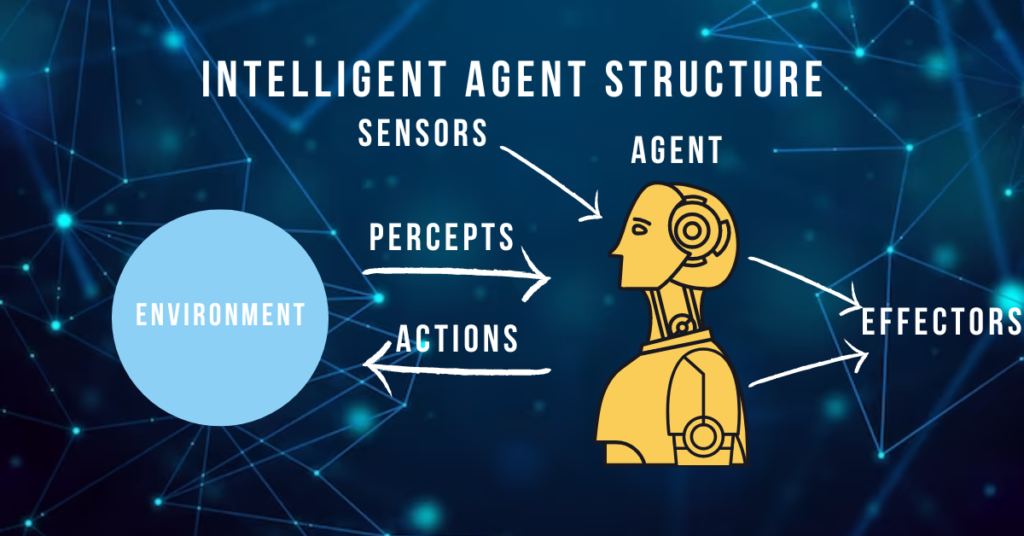
They use sensors to understand what’s happening around them, like eyes and ears for machines. Then, they decide the best course of action based on what they know and have learned before (decision-making processes). Finally, actuators or software interfaces let them act in the real world or online environments.
For instance, autonomous vehicles drive themselves by constantly learning from data about roads and traffic conditions; virtual assistants learn from your requests to provide better responses over time.
These smart machines enhance productivity by automating tasks but also pose challenges such as potential bias in decisions made by AI systems if not carefully designed and monitored for fairness and ethical considerations.
How AI Agents Work?
AI agents perceive their environment, make decisions, and execute actions based on the information they receive – dive in to uncover more about this fascinating topic!
Perception of Environment
AI agents interact with their surroundings using physical or software parts. They use these parts to “see” and “understand” the world around them, much like how your eyes and ears help you make sense of what’s happening.
These agents take in data through sensors — imagine sensors as special eyes for robots or code that acts like ears for software. Then, they figure out what this data means.
You notice changes in your room because of your senses; AI agents do the same with sensors.
After collecting information, AI agents decide on their next move based on what they’ve seen. If a robot detects something new in its path, it decides how to go around it. This is all about making choices wisely and quickly, using the knowledge they have at that moment.
Their reactions are instant, showing us just how smart artificial intelligence can be.

Decision-Making Processes
AI agents look at what’s around them and use data to make smart choices. Think of it as a student picking the best way to solve a math problem by considering different methods. These agents have control systems that help process this information quickly.
They can decide on their own in a changing world, much like how you might choose a different path home if the usual one is blocked.
Next up, they take action based on these decisions. Imagine playing a video game where you decide to dodge an enemy; similarly, AI agents act after making up their minds. Now let’s see what are AI agents, how they move into action….
Execution of Actions
AI agents execute actions by autonomously carrying out tasks in their environment. They use sensors to perceive and understand the world, then make decisions based on that information before utilizing actuators to carry out those decisions.
Through continuous learning, they improve their performance over time.
The execution of actions by AI agents consists of perceiving the environment through sensors, making decisions based on this perception, and finally using actuators to perform these actions.
This entire process happens autonomously without human intervention. The AI agent learns from experience and continuously improves its decision-making capability.
Components of AI Agent Systems
AI agent systems consist of the Agent Function, Sensors and Actuators, and the Knowledge Base. These components work together to perceive the environment, make decisions, and execute actions.
Agent Function
The agent function is the core of an AI agent. It defines how the agent maps inputs to actions within its environment. The function selects an action based on a combination of the current state and any perceptual input at that moment.
In other words, it processes information from sensors to execute appropriate actions using actuators. This helps the AI agent make decisions and act autonomously in pursuit of its goals, ensuring continuous learning and adaptability as it interacts with its environment.
The agent function underpins the entire operation of an AI agent, enabling it to perceive, reason, and act intelligently within real-world scenarios.
By integrating data from various sources such as databases or real-time perceptions, the AI agents can carry out specific tasks like customer service automation or autonomous vehicle control autonomously – enhancing productivity while also raising concerns about potential biases due to their decision-making processes being influenced by societal structures or experiences.

Sensors and Actuators
To grasp data about their surroundings, AI agents utilize sensors. They then take actions based on the decisions made by using actuators. These systems include processors and control units for processing information and making sound decisions.
The integration of sensors facilitates the gathering of essential environmental information which assists in decision-making processes, while actuators are key in turning these decisions into tangible actions.
This combination forms the backbone of the functionality of AI agents, enabling them to interact with and respond to their environment efficiently.
Knowledge Base
The knowledge base in AI agents is like a big library. It stores information learned from previous experiences and data. When the AI needs to make a decision, it searches this library for relevant information to help it choose the best course of action.
This knowledge base can be constantly updated with new facts and insights gained from each interaction or task the AI agent performs. So, as you interact more with them, they become smarter and better at helping you by learning from every experience.
Types of AI Agents
AI agents come in different forms. They include simple reflex agents, model-based reflex agents, goal-based agents, utility-based agents, and learning agents. These diverse types cater to various needs and scenarios where AI is applied.
Simple Reflex Agents
Simple reflex agents operate on a set of pre-defined condition-action rules. They don’t have internal state storage and rely solely on their current perceptions to make decisions and take actions in their environments.
For instance, a simple reflex agent might follow an “if it’s raining, then carry an umbrella” rule without considering whether or not the person actually needs an umbrella based on other factors like temperature or time of day.
In this case, the agent isn’t flexible enough to adapt its behavior based on changing conditions; it strictly follows the programmed rules regardless of any additional information available to it.
Model-Based Reflex Agents
Model-Based Reflex Agents use models of the world to make decisions and update their internal state. They maintain an internal state to keep track of aspects not immediately observable, enabling them to react effectively.
These agents enhance decision-making by using their understanding of the environment.
The model-based reflex agent system includes a knowledge base for storing information about the world, which guides its actions. This architecture enables these agents to analyze situations based on their model and respond accordingly.
For example, in autonomous vehicles, model-based reflex agents utilize their perception of the environment and execute appropriate actions based on this data.
Goal-Based Agents
To understand goal-based agents, it’s important to note that these AI entities determine actions based on achieving specific goals. They go through various stages such as goal initialization, task creation, information gathering, and iteration until the goals are met.
These agents function towards accomplishing a set objective by utilizing their environment perception, decision-making processes, and executing action strategies.
By using this approach, these agents can efficiently navigate complex scenarios to achieve predefined objectives in different applications like supply chain management and autonomous vehicles.
Such rational agent programs focus on maximizing the expected utility derived from decision-making processes and executing appropriate actions toward reaching specific objectives.
Utility-Based Agents
Utility-based agents use utility functions to determine the value of different states. They aim to maximize their utility by selecting actions that lead to the highest possible utility.
These agents consider the desirability of various outcomes and make decisions based on which action will result in the optimal outcome, according to their utility function. For example, an autonomous vehicle might prioritize safety over speed when making driving decisions based on its evaluation of desirable outcomes.
Learning Agents
Learning agents are a type of AI agent that can learn from their environment and improve their performance over time. They adjust their actions based on feedback and experiences. These agents use various techniques such as reinforcement learning and deep learning to continuously enhance their capabilities.
For example, they can be used in autonomous vehicles to adapt to different driving conditions and improve safety.
Learning agents have the ability to make decisions based on past experiences, which makes them suitable for applications where adaptation and continuous improvement are crucial. They are increasingly being used in fields like customer service automation, robotics, and virtual assistants, where the need for adaptive behavior is essential for efficient operations.
This capability allows them to handle complex tasks with changing variables effectively.
Applications of AI Agents
AI agents find applications in diverse areas such as customer service automation and autonomous vehicles. These agents are revolutionizing how businesses operate and deliver services, paving the way for new possibilities in various industries.
Customer Service Automation
Customer service automation uses AI to enhance customer interactions. For example, Amazon Connect Contact Lens automatically detects and redacts sensitive customer data in conversations.
This technology allows supervisors to review human agents and analyze customer sentiments using NLP.
Moving forward, we shall explore the concept of autonomous vehicles.
Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles, like the Waymo self-driving cars, are a prime example of AI agents in action. They use sensors and actuators to navigate and make decisions on the road. These vehicles rely on AI agent technology to perceive their surroundings, decide on actions, and execute them as they move from one point to another.
This means that autonomous vehicles can operate without human intervention, making travel more convenient for you – potentially changing how people get around in the future.
These AI-powered cars are designed with features such as autonomy and continuous learning, which allows them to react and adapt to changes in road conditions while proactively planning their routes.
Through these capabilities, autonomous vehicles offer an exciting glimpse into a future where transportation becomes more efficient, safer, and increasingly automated.
Virtual Assistants
Virtual assistants are AI agents that can help you with tasks like managing to-do lists and conducting research. They use advanced technology to understand your requests and provide helpful responses.
Examples of virtual assistants include AgentGPT, HyperWrite Assistant, Spellpage, and Do Anything Machine.
These virtual assistants can make your life easier by saving time and enhancing productivity in various areas such as task organization and information gathering. With the advancements in AI technology, these virtual assistants continue to improve their capabilities, offering efficient support for daily activities.

Benefits and Risks of AI Agents
AI agents offer the potential for improved productivity and efficiency, streamlining processes, and enhancing customer experiences. They also present risks related to bias and ethical concerns.
I encourage you to read more about these aspects to better understand AI agents’ impact on our future.
Enhanced Productivity and Efficiency
AI agents are transforming the way work gets done. They automate complex tasks, freeing up time for you to focus on more important things. By simplifying workflows and acting autonomously, they reduce your workload and improve efficiency.
These digital assistants can handle repetitive tasks with precision and accuracy, offering consistent performance around the clock. Integrating AI agents into your operations can help enhance productivity by streamlining processes and optimizing resource utilization.
With these tools at your disposal, you’re poised to achieve higher levels of output with fewer resources– ultimately boosting overall efficiency.
Potential for Bias and Ethical Concerns
AI agents have the potential to perpetuate bias and make unfair decisions if not carefully designed and monitored. This could result in discrimination against certain groups of people based on race, gender, or other characteristics.
For example, biased AI algorithms used in recruiting software may unintentionally favor male candidates over female ones. Addressing these concerns is crucial to ensure fairness and prevent discrimination.
Furthermore, ethical challenges related to AI agents include safeguarding data privacy and avoiding harmful influence on society. Without proper safeguards and regulations, AI agents may compromise individuals’ privacy by mishandling sensitive information.
Therefore, it’s essential to establish clear guidelines for data protection and ethical usage of AI technologies to minimize these risks.

The Future of AI Agents
The future of AI agents lies in their integration into our daily lives, impacting employment and industry. Their influence will be far-reaching. Read more to understand the transformation they bring!
Integration into Daily Life
AI agents are becoming an everyday part of life. You will notice them in customer service, healthcare, and even at home. For instance, AI agents can help you with daily tasks like setting reminders or managing your shopping list.
They also have a big role in industries such as retail, transportation, and finance.
The integration of AI agents into your daily life is already happening. From smart homes to virtual assistants on your phone, these intelligent systems are becoming more prevalent and shaping the future of various aspects of daily living.
Impact on Employment and Industry
AI agents will revolutionize industry practices and jobs, with potential shifts in how people interact with technology. Commercial AI agent platforms entering the market could lead to significant changes, affecting roles and operations across various sectors.
The widespread utilization of AI agents may drive increased efficiency but also necessitate adjustments in labor dynamics and retraining needs as tasks become automated or augmented by intelligent systems.
The introduction of AI agents into industries like customer service, logistics, and process automation indicates a future where human-machine collaboration plays a critical role. However, it also raises concerns about biases and ethical considerations embedded within these technologies.
As AI agent systems become more prevalent in everyday life, their impact on employment disparities necessitates continuous monitoring to ensure balanced integration that benefits both businesses and workers.

Conclusion – What are AI Agents?
Now you know what are AI agents.
In the future, AI agents will revolutionize the way we interact with technology. They are software programs that can gather data and perform tasks independently to achieve specific goals.
These AI agents have various types such as simple reflex agents, model-based reflex agents, goal-based agents, utility-based agents, learning agents, and hierarchical agents. Despite their limitations in processing long-form content effectively, they will significantly impact our daily lives and industries.
Embrace this trend for a more efficient and innovative future!
FAQs – What are AI Agents
1. What are AI agents?
AI agents, also known as intelligent or autonomous agents, are computer programs that can make decisions and solve problems on their own. They use machine learning algorithms and large language models to process information from the internet or other sources.
2. How do AI Agents work?
AI Agents rely on reasoning and percepts for decision making. They might use rational agent techniques like belief-desire-intention or simple-reflex methods… all depending on the objective function they’re programmed to achieve.
3. Can AI agents interact with humans?
Yes! With advancements in natural language processing and generative artificial intelligence like ChatGPT by OpenAI’s, AI chatbots can now mimic human conversation… even understanding customer behavior!
4. Are there different types of AI Agents?
Absolutely! From software agents handling analytics tasks to multimodal ones capable of complex problem-solving in multi-agent systems – each one is a unique blend of technical complexities.
5. Is there any downside to using AI Agents?
While they offer many benefits, it’s important to be aware of potential algorithmic bias stemming from the training data used… The strong AI hypothesis argues that these biases could limit an artificial general intelligence’s ability to truly replicate human intelligence.
6. How will AI Agents change our future?
From Alphago beating world champion Go players, robotic process automation revolutionizing industries, up until apps driven by abstract intelligent agents – the possibilities seem endless! But remember: As we move towards this future with autonomous intelligent agent technology taking center stage; oversight remains crucial.





