Knowing what is data storage in today’s digital world is important to protect your personal data and operating a business.
In its most basic form, data storage is the act of storing digital information in order to make it accessible and useful at a later time. The volume of data generated by organizations and individuals has increased dramatically in recent years, with over 2.3 billion people using data storage. As such, the need for effective and efficient data storage solutions as the requirement for data storage has grown tremendously.
To understand what data storage is, it’s important to first understand the fundamentals of data. Data is any piece of information that can be stored and processed by a computer. This can include everything from text documents and images to videos and audio files. Data storage involves finding ways to store this information so that it can be accessed and used later. There are many different types of data storage solutions available, each with their own advantages and disadvantages.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Data storage involves recording and preserving digital information for future use.
- There are many different types of data storage solutions available, each with their own advantages and disadvantages.
- Effective and efficient data storage solutions are becoming increasingly important as the amount of data being generated continues to increase.
What is Data Storage?
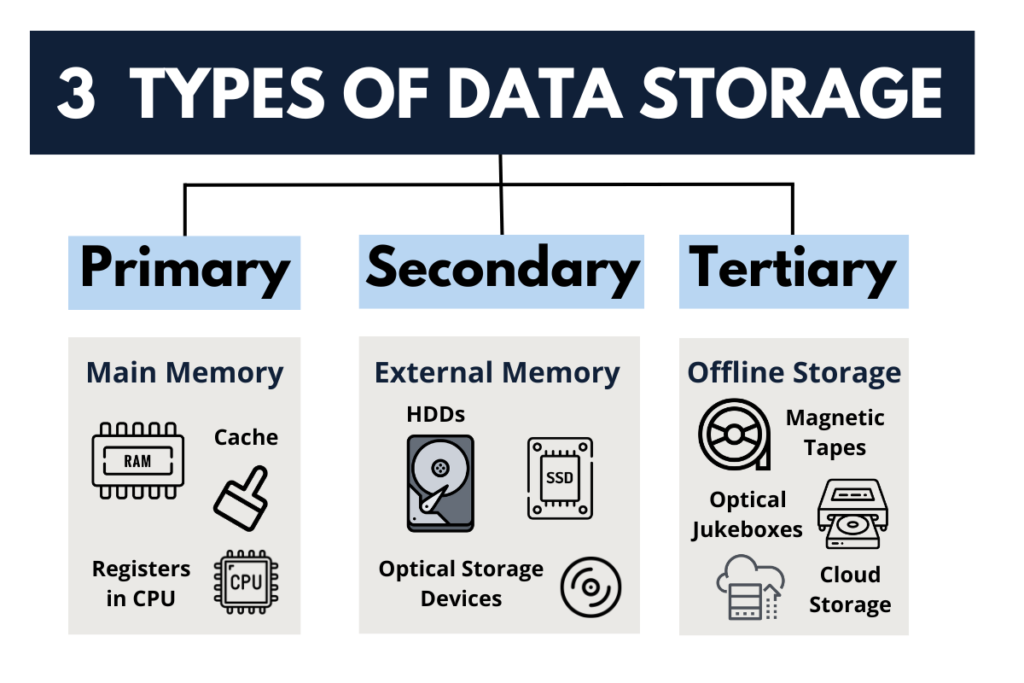
Data storage is the process of saving digital information on various types of storage media. Data storage can be classified into three types.
Primary storage is also known as volatile storage, which refers to temporary storage that is used by the CPU to access data actively.
In contrast, secondary storage, also known as non-volatile storage, is used to store data for future use.
Tertiary storage refers to a type of data storage that uses removable media, such as tape drives or optical discs, for long-term data archiving and backup purposes.
There are various types of storage media used for data storage. Some of the most common storage media include magnetic, optical, and mechanical media. Magnetic storage media include hard disk drives (HDDs) and magnetic tapes. Optical storage media include CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs. Mechanical storage media include solid-state drives (SSDs) and USB drives.
In addition to storage media, data storage also involves data organization and management. Data organization refers to the process of arranging data in a logical and coherent manner, making it easier for users to access and manage the data. Data management, on the other hand, involves the processes of storing, protecting, and backing up data to ensure its availability and integrity.
Overall, data storage is an essential component of modern computing systems. It enables you to save and access data for future use, making it easier to manage and process large amounts of information.
Types of Data Storage
There are various types of data storage available, each with its own benefits and limitations.
Here are some of the most common types of data storage:
Hard Disk Drives
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) are one of the most common types of data storage. They use magnetic disks to store data and are available in various sizes, speeds, and capacities. HDDs are relatively cheap and can store large amounts of data. However, they could be physically damaged.
Solid-State Drives
Solid-State Drives (SSDs) are becoming increasingly popular due to their faster speeds and reliability. SSDs use flash memory to store data, making them more durable and less prone to damage and failure. They are also faster than HDDs and have no moving parts, making them quieter and more energy-efficient. However, they are more expensive than HDDs and have lower storage capacities.
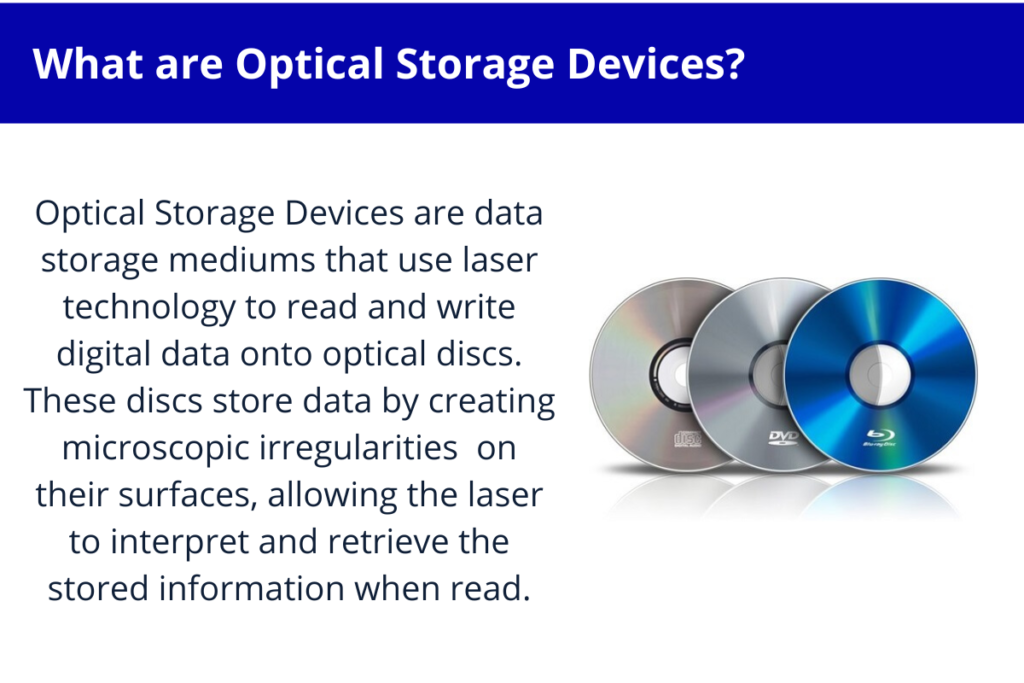
Optical Storage
Optical Storage uses lasers to read and write data to CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs. Its is relatively inexpensive and can store large amounts of data. However, it is slower than other types of data storage and can be affected by scratches, dust, and other contaminants.
Flash Memory
Flash Memory is a type of non-volatile memory that can be erased and reprogrammed. Flash memory is commonly used in USB drives, memory cards, and solid-state drives. Flash memory is faster and more reliable than traditional hard drives, but it has a limited lifespan and can be affected by temperature and humidity.
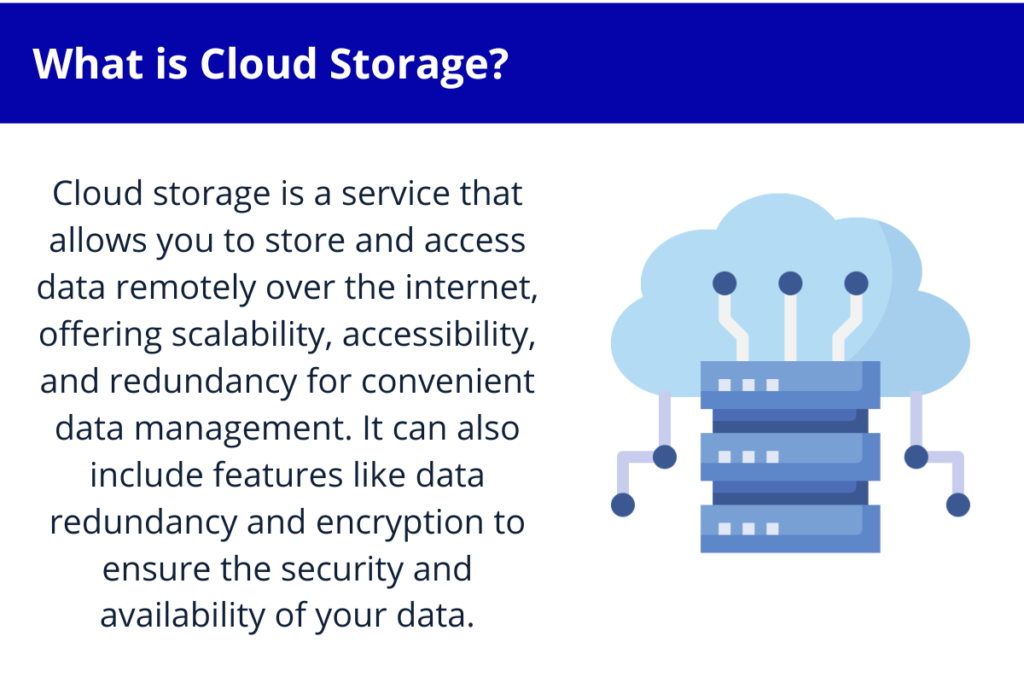
Cloud Storage
Cloud Storage is a type of data storage that allows you to store and access data over the internet. Cloud storage is becoming increasingly popular due to its convenience, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Cloud storage providers offer various storage options, including file storage, object storage, and block storage. However, cloud storage can be affected by internet connectivity issues and security concerns.
The most popular cloud storage services include Dropbox, Sync.com and pCloud.
Data Storage Devices
When it comes to storing data, there are a variety of devices to choose from, each with its own unique benefits and drawbacks. Here are some common types of data storage devices:
External Storage Devices
External storage devices are portable devices that can be connected to your computer or other device to provide additional storage space. These devices typically use USB or Thunderbolt connections to transfer data. External hard drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), and USB flash drives are all examples of external storage devices.
External storage devices are ideal for backing up important data or for transferring large files between devices. They are also useful for people who need to work on multiple devices and want to be able to access their files from anywhere.
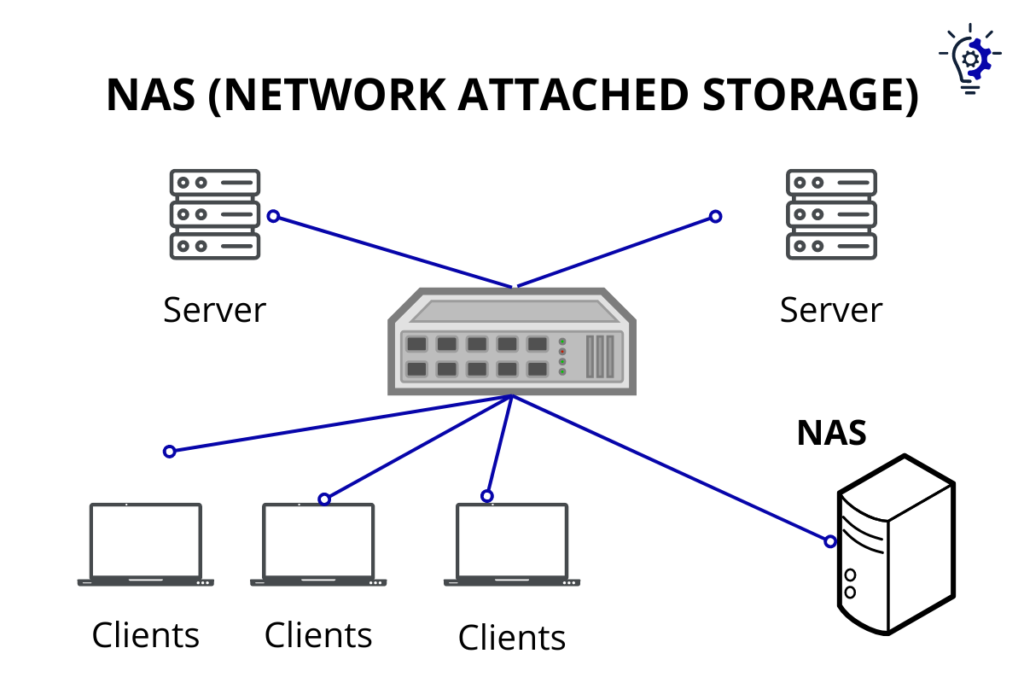
Network-Attached Storage
Network-attached storage (NAS) is a type of storage device that is connected to a network rather than to a single computer. This allows multiple users to access the same data at the same time. NAS devices are often used in small businesses or homes with multiple computers.
NAS devices typically have multiple hard drives that can be configured in a variety of ways, such as RAID (redundant array of independent disks). This provides data redundancy, which means that if one drive fails, the data can still be accessed from the other drives.
You can even use NAS to store your favorite movies. You can set up your NAS with Plex.
Storage Area Networks
Storage area networks (SANs) are a type of high-speed network that provides block-level access to data storage. SANs are typically used in large enterprises that require high-performance storage for mission-critical applications.
SANs use a dedicated network that is separate from the regular network used by the organization. This allows for faster data transfer rates and reduces the risk of network congestion.
File Systems and Databases
When it comes to data storage, there are two main types: file systems and databases. Both serve the same purpose of storing data, but they differ in how they organize and manage your data.
File System Types
File systems are the most basic form of data storage and are used to store files on a computer or server. There are several types of file systems, including:
- FAT (File Allocation Table): This is the oldest and simplest file system and is used on older versions of Windows. It has limitations in terms of file size and partition size.
- NTFS (New Technology File System): This is the current file system used on Windows and is more advanced than FAT. It supports larger file sizes, better security, and more efficient use of disk space.
- HFS (Hierarchical File System): This is the file system used on Apple’s macOS. It is similar to NTFS in terms of features and functionality.
File systems are best suited for storing unstructured data, such as documents, images, and videos. They are not ideal for storing structured data, such as customer information or financial data, which requires more advanced management and querying capabilities.
Database Storage Models
Databases are a more advanced form of data storage and are designed to store structured data. There are several types of database storage models, including:
- Relational Databases: This is the most common type of database and is based on the relational model. Data is stored in tables, with each table representing a specific entity, such as customers or orders. Tables are linked together using keys, which allows for complex queries and analysis.
- NoSQL Databases: This is a newer type of database that is designed to handle unstructured and semi-structured data. NoSQL databases use a variety of data models, including document, key-value, and graph, to store data.
Databases are best suited for storing structured data, such as customer information, financial data, and inventory management. They offer advanced querying and management capabilities, making it easier to analyze and extract insights from the data.
Both have their own strengths and weaknesses, and the choice between them depends on the type of data being stored and how it will be used.
What is Data Storage Capacity and Units
When it comes to data storage, capacity is an important factor to consider. Capacity refers to the amount of data that can be stored on a device or system. The unit of measurement for data storage capacity is the byte. A byte is a unit of digital information that consists of eight bits.
There are several units of measurement used to describe data storage capacity. The most common units are:
- Bit: The smallest unit of digital information. A single bit can store a value of either 0 or 1.
- Byte: A unit of digital information that consists of eight bits. A single byte can represent a single character, such as a letter or number.
- Kilobyte (KB): 1,024 bytes.
- Megabyte (MB): 1,024 kilobytes, or 1,048,576 bytes.
- Gigabyte (GB): 1,024 megabytes, or 1,073,741,824 bytes.
- Terabyte (TB): 1,024 gigabytes, or 1,099,511,627,776 bytes.
- Petabyte (PB): 1,024 terabytes, or 1,125,899,906,842,624 bytes.
- Exabyte (EB): 1,024 petabytes, or 1,152,921,504,606,846,976 bytes.
As you can see, the units of measurement increase exponentially as you move up the scale. This means that a single terabyte can store a lot more data than a single gigabyte, and so on.
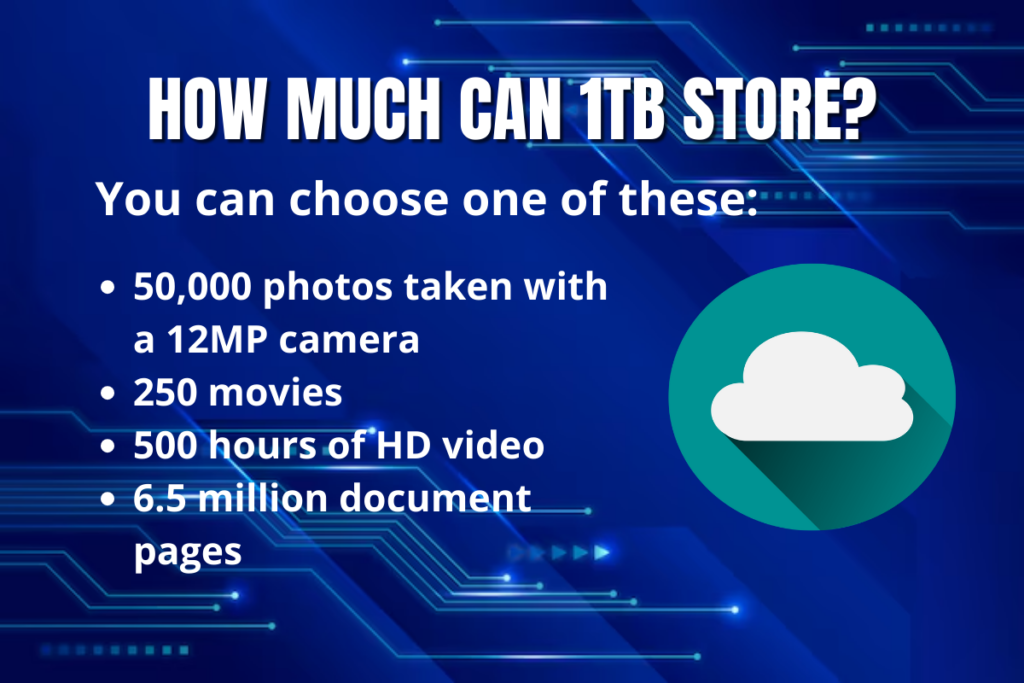
When you’re choosing a data storage solution, it’s important to consider how much data you need to store and how quickly you’ll need to access it. If you’re dealing with large amounts of data, you may need to consider a solution that offers multiple terabytes or even petabytes of storage capacity.
Data Accessibility and Retrieval
Once data is stored, it needs to be easily accessible and retrievable. This is where data storage solutions come into play.
For example, if data is stored on a hard drive, it can be accessed quickly but may be vulnerable to physical damage. On the other hand, if data is stored on a cloud-based storage solution, it may take longer to access but is more secure and can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
One way to ensure data accessibility and retrieval is to use a hierarchical storage management system. This system automatically moves data between different storage tiers based on its frequency of access. Frequently accessed data is stored on faster, more expensive storage, while less frequently accessed data is stored on slower, less expensive storage. This can help balance the need for quick access to data with the need to keep storage costs under control.
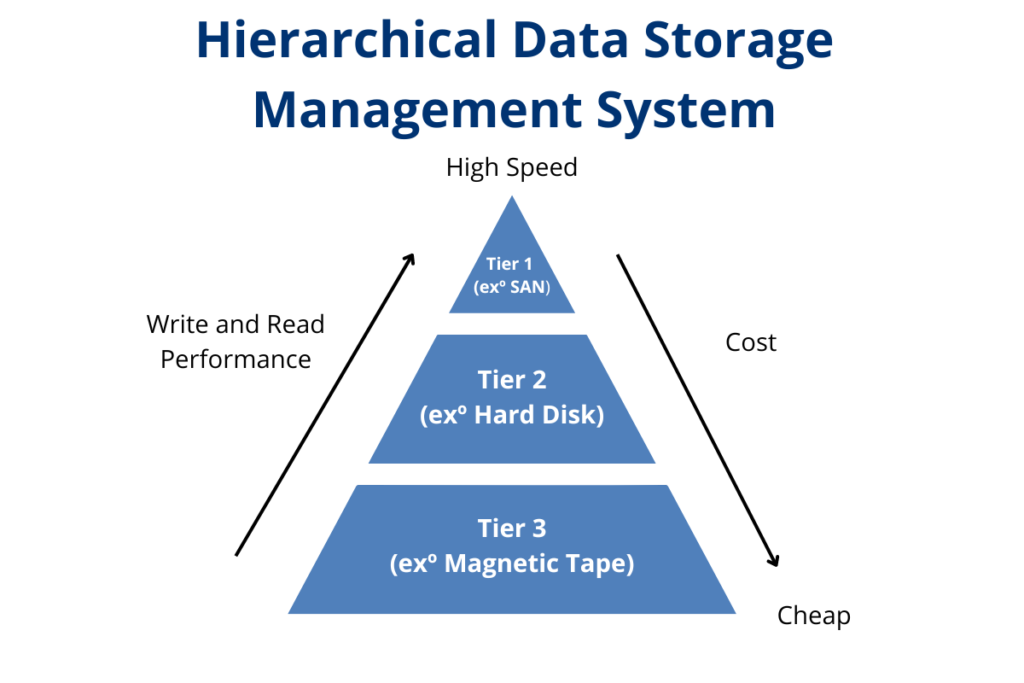
Another important consideration for data accessibility and retrieval is data backup and disaster recovery. It is important to have a backup of your data in case of hardware failure, cyberattacks, or natural disasters. This backup should be stored in a separate location from the original data to ensure it is not affected by the same disaster. Cloud-based backup solutions are becoming increasingly popular as they offer secure, off-site storage that can be accessed from anywhere. This is from where the three data storage rule is from.
By choosing the right storage solution, implementing a hierarchical storage management system, and having a backup and disaster recovery plan in place, you can ensure your data is always accessible and retrievable when you need it.
Data Security and Encryption
When it comes to data storage, security is of utmost importance. Data security refers to the protection of digital data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. Proper data security measures ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive information.
One of the most important aspects of data security is encryption. Data encryption is the process of converting plain text into a secret code that can only be deciphered with a key. This ensures that even if a hacker gains access to your data, they won’t be able to read it without the key. Encryption is used to protect sensitive data such as financial information, medical records, and personal information.
There are two main types of encryption: symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric encryption uses a single key to encrypt and decrypt data. Asymmetric encryption uses two keys – a public key to encrypt data and a private key to decrypt it. Asymmetric encryption is more secure than symmetric encryption, but it’s also more complex and slower.
There are also other security measures, like data masking or tokenization. And please remember that they are not the same as encryption. Each has its own characteristics and use cases.

In addition to encryption, there are several other measures that can be taken to ensure data security. These include access controls, firewalls, and antivirus software. Access controls limit who can access data and what they can do with it. Firewalls protect against unauthorized access to a network, while antivirus software detects and removes malicious software that can compromise data security.
Overall, data security and encryption are crucial components of data storage. By implementing proper security measures, you can ensure that your data is protected from unauthorized access and use.
Data Redundancy and Backup
When it comes to data storage, redundancy and backup are two important concepts that can help you protect your data. In this section, we’ll explore what these terms mean and how they differ.
RAID Systems
One way to achieve data redundancy is through the use of RAID systems. RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks, and it’s a technology that allows you to combine multiple hard drives into a single logical unit. There are several different RAID levels, each with its own benefits and drawbacks.
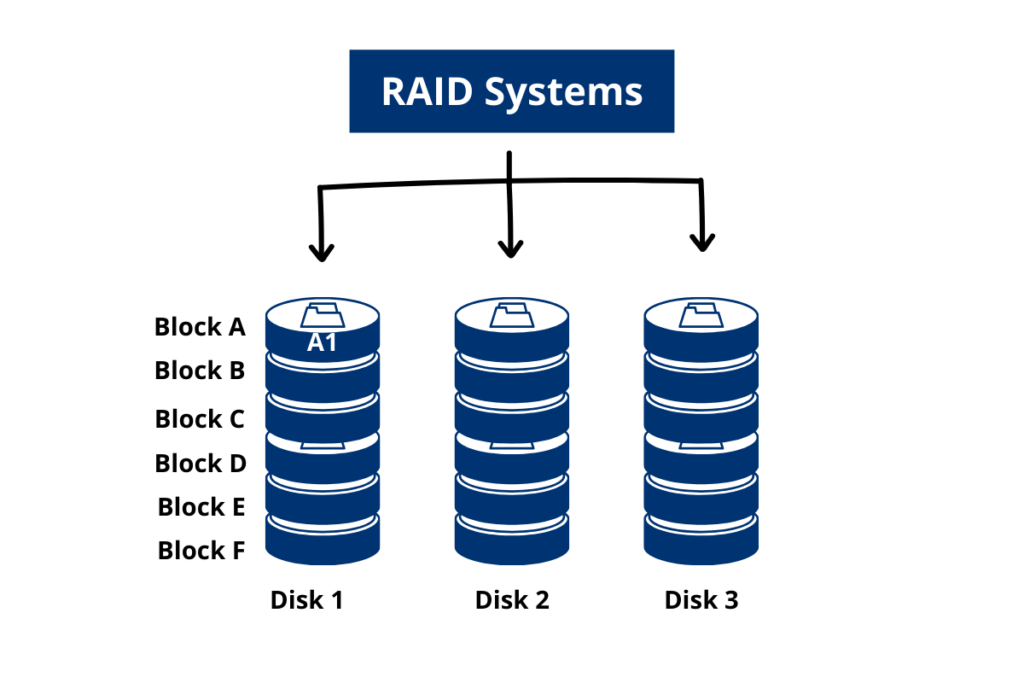
For example, RAID 1 is a simple mirroring solution that creates an exact copy of your data on two separate hard drives. If one drive fails, you can still access your data from the other drive. RAID 5, on the other hand, uses parity data to protect against data loss. If one drive fails, the missing data can be reconstructed from the parity data and the remaining drives.
You can know more about RAID Systems and calculate the data storage capacity of your RAID system with this calculator. I think this can help you a lot.
Data Replication
Another way to achieve data redundancy is through data replication. This involves creating multiple copies of your data and storing them in different locations. For example, you might replicate your data across multiple servers in different geographic locations. This can help protect against data loss due to natural disasters, power outages, or other events that might affect a single location.
Backup Solutions
While redundancy can help protect against data loss, it’s not a complete solution. That’s where backups come in. A backup is a copy of your data that’s stored separately from your primary data. If your primary data is lost or corrupted, you can restore it from your backup.
There are many different backup solutions available, ranging from simple file-based backups to more complex solutions that backup entire systems. Some backup solutions even offer features like versioning, which allows you to restore previous versions of your data.
In conclusion, data redundancy and backup are both important concepts to consider when it comes to data storage. By implementing redundancy and backups, you can help protect your data from loss due to hardware failure, natural disasters, or other events.

Emerging Technologies in Data Storage
Data storage technology has come a long way over the years, and it continues to evolve at a rapid pace. Emerging technologies in data storage are changing the way we store, manage, and access data. Here are some of the most significant emerging technologies in data storage:
Hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI)
Hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) is a software-defined infrastructure that combines compute, storage, and networking into a single system. HCI is becoming increasingly popular in data centers because it simplifies management and reduces costs. With HCI, you can scale up or down by adding or removing nodes, which makes it easy to manage your infrastructure.
Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe)
Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) is a storage interface that provides faster access to data than traditional storage interfaces like SSD SATA and SAS. NVMe uses a high-speed PCIe interface, which allows it to take advantage of the full bandwidth of modern CPUs. NVMe is becoming increasingly popular in high-performance computing and enterprise storage environments, like in SSD components.

Edge Storage
Edge storage is a type of storage that is located at the edge of a network, close to where data is generated. Edge storage is becoming increasingly important as more and more data is generated at the edge of the network. With edge storage, you can store and process data locally, which reduces latency and improves performance.
Object Storage
Object storage is a type of storage that stores data as objects rather than files or blocks. Object storage is becoming increasingly popular in cloud storage environments because it is highly scalable and can store massive amounts of data. Object storage is also highly resilient, which makes it ideal for storing data that needs to be highly available.
Tape Storage
Tape storage is a type of storage that uses magnetic tape to store data. Tape storage is becoming increasingly popular in long-term storage environments because it is highly reliable and cost-effective. Tape storage is also highly scalable, which makes it ideal for storing large amounts of data over long periods of time.
Overall, these emerging technologies in data storage are changing the way we store, manage, and access data. As data continues to grow at an exponential rate, it is becoming increasingly important to have storage solutions that are scalable, reliable, and cost-effective. With these emerging technologies, you can build storage solutions that meet the needs of your organization, both now and in the future.

Frequently Asked Questions – What is data storage?
What are the different types of data storage available?
There are several types of data storage available, including primary, secondary, and tertiary storage. Primary storage, or memory, is the area in a computer where data is stored for quick access by the computer’s processor. Secondary storage, such as hard disk drives (HDD) and solid-state drives (SSD), is used to store data that is not currently being used by the processor. Tertiary storage, such as tape drives, is used for long-term storage of data that is rarely accessed.
How does data storage work in modern computers?
Modern computers use a combination of primary and secondary storage to store and access data. When you save a file, it is stored on the secondary storage device, such as an HDD or SSD, and is then loaded into primary storage, or memory, when you open the file. When you are finished with the file, it is saved back to the secondary storage device for future access.
What are the primary purposes of data storage?
The primary purposes of data storage are to provide a place to store data and to make that data easily accessible. Data storage also provides a way to protect data from loss or corruption.
What factors should be considered when choosing a data storage solution?
When choosing a data storage solution, several factors should be considered, including capacity, speed, reliability, and cost. The amount of data you need to store, the speed at which you need to access that data, and the importance of that data will all play a role in determining the best storage solution for your needs.
Can you provide some common examples of data storage devices?
Common examples of data storage devices include hard disk drives (HDD), solid-state drives (SSD), USB flash drives, memory cards, and optical discs such as CDs and DVDs.
How has data storage technology evolved over time?
Data storage technology has evolved significantly over time, from early magnetic tape drives and floppy disks to modern solid-state drives and cloud storage solutions. As technology has improved, data storage devices have become smaller, faster, and more reliable, allowing for more data to be stored in less physical space.
Conclusion – What is data storage?
As we’ve explored “What is data storage,” it’s clear that the field is always changing, making it crucial to choose secure and efficient storage options. By following best practices, like regular backups and using modern encryption, we can keep our digital information safe and accessible. Understanding “What is data storage” is essential in today’s data-driven world, and selecting the right solutions helps protect our digital assets. For more on “What is data storage” and how to make the most of your data, check out my other articles.
If you have any further questions or require additional assistance, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us through our contact page.