Are you worried about losing your data? The 3-2-1 Data Storage Backup Rule is a proven method. This article will show how it protects your files from disaster by using simple steps. Stay safe and read on.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- The 3-2-1 Data Storage Backup Rule helps keep your files safe. It says to have three copies of your data, use two types of storage, and keep one backup in a different place.
- Using cloud services and different devices like hard drives or USB sticks makes sure you can get your files back even if something bad happens.
- Putting the backup plan into action involves picking the right tools and places to store your data so it stays safe but still easy to reach when needed.
- Cloud solutions add an extra layer of safety by keeping your important files off-site. This means less risk of losing them in disasters like fire or theft.
- Regularly updating and checking backups is crucial for making sure all your important information remains protected no matter what happens.
Understanding the 3-2-1 Data Storage Backup Rule

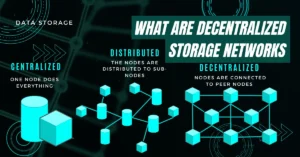
The 3-2-1 backup rule is simple but crucial for keeping your files safe. It means you should have three total copies of your data, use two different types of storage devices like an external disk and cloud service, and keep one copy in a different place, away from the others.
What is the 3-2-1 Data Storage Backup Rule?
The 3-2-1 Backup Rule is a simple yet powerful strategy for protecting data. It suggests keeping three copies of your digital files. Use two different storage types, like hard drives and cloud services, ensuring your data stays safe even if one fails.
Always have one copy stored off-site or in the cloud to protect against disasters at your main location. U.S. photographer Peter Krogh crafted this rule nearly two decades ago, earning endorsements from both the United States government and Carnegie Mellon University for its effectiveness in safeguarding information security.
Organizations often build on this foundation, opting for more than three copies to further secure their digital assets against data loss events such as cyberattacks or system failures.
By following these steps — creating multiple backups, diversifying storage media, and separating storage locations — businesses and individuals significantly reduce risks associated with losing critical digital information.
Components: 3 Copies, 2 Media Types, 1 Off-site Location
You need three copies of your data. This ensures if one copy fails, you have two more. Store these on two different types of media – like cloud storage and an external hard drive. It makes sure problems with one type won’t affect both copies.
Always keep one backup in a different place, away from the others. This could be off-site storage or online in the cloud. If something bad happens at your main location, like fire or theft, you still have your data safe somewhere else.
Always back up your data in three places: on two kinds of devices and in another location.
Implementing the 3-2-1 Backup Strategy

Putting the 3-2-1 backup plan into action means picking where and how to store your copies. You’ll need things like cloud services, external hard drives, or maybe even USB sticks for this step.
Simple Steps to Backup your Data efficiently
Effective data backup is crucial for protecting against data loss. It ensures business continuity and safeguards against cyber threats like ransomware attacks. Here are steps to achieve this:
- Assess your data. Identify what’s critical to back up, such as databases, customer information, and financial records.
- Choose reliable backup software. Tools like Acronis Cyber Protect Home Office and Veeam can automate the process.
- Follow the 3-2-1 rule. Make three copies of your data, use two different storage types, and keep one copy off-site.
- Use cloud services for off-site backups. Options include Dropbox, Sync.com and pCloud, which offer secure storage outside your primary location.
- Schedule regular backups. Incremental backups should happen daily, with full backups weekly or monthly.
- Verify backups regularly to ensure they’re error-free. Recovery verification can confirm zero errors in your backup copies.
- Secure your backups with encryption to protect against unauthorized access, especially for sensitive information.
- Embrace continuous data protection (CDP) for real-time backing up of all changes made to data.
- Utilize deduplication technology to reduce storage space by eliminating duplicate copies of the same file across backups.
- Plan for quick recovery by setting clear objectives for how fast you need to recover (Recovery Time Objective) and how much data you can afford to lose (Recovery Point Objective).
By taking these steps, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of losing important information due to hardware failure, natural disaster, or cybercrime incidents like ransomware attacks and ensure they have secure means for disaster recovery and business continuity planning through efficient backup management systems
Select Appropriate Media and Backup Locations
Choosing the right media and locations for backups ensures data stays safe. It balances security with accessibility. Here’s how to do it:
- Look at cloud services like Seagate Lyve Cloud for off-site backups. Cloud options provide instant access and protect against physical disasters.
- Use different media types – hard drives, USB flash drives, and optical disks. This diversity keeps data secure even if one type fails.
- Consider hybrid cloud solutions for businesses. They merge on-premises and cloud storage, offering flexibility.
- Backup data in multiple locations — one on-site for quick recovery and another off-site for disaster protection.
- Schedule regular back-ups to avoid losing recent data changes or additions.
- Use services that offer multiple zones for data storage; this ensures your data is available even if one zone goes down.
- Encrypt sensitive files before backing them up to enhance security further.
- Prioritize backups based on file importance, ensuring critical data gets backed up first.
- Verify backups routinely to confirm files are intact and recoverable.
- Leverage network-attached storage (NAS) devices for an easily accessible but secure on-premises option.
Now, let’s explore integrating cloud solutions more deeply.
Adapting the 3-2-1 Data Storage Backup Rule for Modern Needs
The 3-2-1 backup rule isn’t stuck in the past; it evolves with tech changes. Now, we add cloud storage and hybrid systems to keep data safer than ever.
Integrating Cloud Solutions: The 3-2-1-1-0 Model
Cloud solutions now play a big role in the 3-2-1-1-0 model. Veeam adds extra layers with one copy offline, air-gapped, or immutable and zero errors during recovery checks. This way, data stays safe and easy to get back if lost.
Cloud storage like Dropbox or pCloud helps keep an off-site backup without trouble. Using multiple cloud providers increases chances of getting data back after a problem.
Businesses use both private and public cloud options for more safety. They make sure backups are not only saved but also protected from cyber threats. With partners like Veeam, companies can set up strong backups that hackers can’t change or delete.
Next, we’ll explore why sticking to this plan is crucial for keeping data secure.
Hybrid Cloud Options for Businesses
Hybrid cloud options blend private clouds, public services, and on-premise resources. This mix gives businesses flexibility and more control over their data. Companies can keep sensitive information in the private cloud while using the public cloud for less critical data.
You can use DigitalOcean or Linode as your cloud hosting platforms
This approach allows for scaling resources up or down as needed, which saves money and improves efficiency.
A hybrid cloud strategy offers the best of both worlds, combining the security of private clouds with the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public clouds.
Businesses use this model to back up data securely while ensuring quick access to it when necessary. Hybrid clouds support various applications and workloads, moving them between different environments depending on demand and cost factors.
Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) is a key feature here; it protects critical systems without needing physical hardware transport or complex logistics.
The Importance of Following the 3-2-1 Data Storage Backup Rule
Keeping your files safe is key. The 3-2-1 Data Storage Backup Rule helps stop you from losing important stuff if something bad happens.
Safeguarding Data Integrity and Security
Keeping your files safe is a must. With 3-2-1 backup, data stays secure and intact. Amazon S3 Object Lock and Azure Blob have special features. They make backups unchangeable. This fights against unwanted changes or deletions.
Seagate offers great backup tools at good prices. These tools help keep your data safe in different places.
Veeam’s Rick Vanover knows how to keep data available all the time. Using cloud solutions makes the 3-2-1 rule even stronger against loss from hardware issues or disasters. Next, we talk about how less chance of losing data helps everyone.
Reducing the Risk of Data Loss
Data loss is a big risk. The 3-2-1 backup rule cuts this risk by keeping three copies of data, using two different storage types, and making sure one copy is off-site. This method protects against disasters like fires or theft.
Cloud services play a key role here. Companies like Backblaze offer secure online backups with features such as Extended Version History to protect data even more.
Here you can learn how to protect your cloud storage safety.
With the 3-2-1 strategy, updating and checking backups often are crucial steps. For example, creating regular duplicate files on both physical drives and cloud platforms ensures safety from many threats.
Also, storing one version in a distant location guards against local problems wiping out all copies at once. This approach makes sure that important information stays safe no matter what happens.
Conclusion
The 3-2-1 Backup Rule saves your day when tech disasters hit. It means three copies of your files, on two different storage kinds, with one located far away. This simple rule stands like a strong wall between your data and threats like crashes or hacks.
Cloud backups add more safety, making sure you can get back what’s lost without a sweat. The point is clear: For secure and easy file recovery after a mishap, the 3-2-1 strategy is key.

FAQs
1. What does the 3-2-1 Data Storage Backup Rule rule mean?
The 3-2-1 backup rule means keeping three copies of your data, on two different types of media, with one copy stored offsite for safety.
2. Why is following the 3-2-1 Data Storage Backup Rule important?
Following this rule protects against data loss by ensuring multiple recovery points and formats, reducing risks from disasters or failures.
3. How can I apply the 3-2-1 rule to my data storage strategy?
Start by creating three backups of your critical files. Use devices like USB drives and cloud storage services for diversity. Keep one backup in a different location, maybe a cloud service or an external drive at another site.
4. What are some examples of storage media I can use for my backups?
Examples include internal hard drives, external USB drives, Blu-ray discs, and cloud-based platforms like internet-connected cloud infrastructure or object storage services.
5. Can the 3-2-1 Data Storage Backup Rule help during a system outage?
Yes! Having multiple backups across different locations ensures you can recover essential data quickly after an outage, minimizing downtime.
6. Does implementing a 3-2-1 backup approach prevent malware attacks?
While it doesn’t stop attacks, it significantly enhances your ability to recover from such incidents without losing valuable information.