Having trouble keeping your files safe? You should know what is Cloud Backup.
Cloud backup offers a reliable solution for protecting against data loss and ensuring quick recovery after a disaster. This comprehensive guide for beginners will walk you through what cloud backup is, how it works, and why it’s essential for both personal use and business continuity.
Keep reading to discover everything you need to know about securing your data storage.
Key Takeaways
- Cloud backup stores your data on remote servers, making it easy to recover files after a disaster.
- It is cost-effective and offers more flexibility than traditional methods, which require physical storage.
- You can access cloud-backed-up data from anywhere at any time if you have an internet connection.
- Hybrid cloud backup combines public, private clouds, and on-premises solutions for better data protection.
- When choosing a cloud backup service, consider security features like encryption and multi-factor authentication to keep your information safe.
Table of Contents
What is cloud backup and how does it work?
Cloud backup is a method of storing data on remote servers accessed via the internet, ensuring it’s available for retrieval whenever needed. It works by automatically duplicating and transferring data to an off-site server for safekeeping and easy access.
Definition of cloud backup
Cloud backup involves storing your important data, like files and documents, on remote servers. These servers are managed by third-party services. This method is also known from terms such as online backup or remote backup.
It means you’re sending a copy of your digital stuff to a place off-site. By doing this, your data gets stored safely away from your main location.
Imagine you’re working on a big school project with lots of videos and presentations saved on your computer. If something bad happens to your computer, all that hard work could be lost forever.
But if you use cloud backup, you send copies of those videos and presentations over the internet to secure storage spaces managed by companies that specialize in keeping data safe.
This way, even if disaster strikes at home or at school, you can still get back all your projects quickly because they are safely backed up in the cloud.
How it differs from traditional backup methods
Now that you understand the definition of cloud backup, let’s talk about how it differs from traditional backup methods. Unlike traditional backups, where data is stored on physical devices like hard drives or tapes, cloud backup stores data on remote servers accessible via the internet.
This means you don’t need to worry about maintaining hardware or transporting physical storage devices for off-site protection. Additionally, cloud backup services often provide automated and continuous backups, ensuring that your data is consistently up to date without manual intervention.
With traditional methods, periodic backups are typically performed at scheduled intervals or manually by individuals. Cloud backup offers a more flexible and convenient approach to safeguarding your important information.

Image by kjpargeter on Freepik
Remember – files would not be saved during an office flood if we solely relied on local backups!
How data is backed up to the cloud
To back up your data to the cloud, you can follow these steps:
- Sign up for a cloud backup service that suits your needs and budget.
- Install the backup software provided by the service on your device.
- Select the files and folders you want to back up to the cloud. You should keep them organized.
- Schedule automatic backups at regular intervals to ensure all new data is consistently backed up. Use the 3-2-1 data storage backup rule.
- Ensure a secure internet connection during the backup process to protect your data.
This comprehensive guide equips you with essential knowledge about backing up your data in the cloud.
Benefits and Use Cases of Cloud Backup
Cloud backup provides cost-effective data protection and disaster recovery strategies, ensuring increased accessibility to your information whenever you need it.
Cost-effectiveness
Cloud backup is cost-effective for businesses because it eliminates the need to invest in physical infrastructure and additional resources for data storage. By using a cloud backup service, you can avoid large upfront capital investments and only pay for the space you use, allowing for flexible scalability without excessive costs.
It also reduces operational expenses associated with managing on-premises backup solutions, making it a budget-friendly option that caters to your specific needs.
Considering these benefits of cost-effectiveness, let’s now delve into how cloud backup offers increased accessibility for businesses like yours.
Increased accessibility
With cloud backup, you have increased accessibility to your data. It allows you to access your important files and documents from anywhere, at any time, as long as you have an internet connection.
This flexibility ensures that you can work on your files or retrieve information even when you’re not in the office. Cloud backup also enables businesses to maintain their operations seamlessly, no matter where they are located or what time it is.
So, it’s like having a virtual database that travels with you wherever you go.
By using cloud backup, users gain internet access flexibility for their data storage needs and prevention of data loss.
Disaster recovery strategies
In the event of a disaster, having effective recovery strategies in place is crucial. Cloud backup enables you to quickly recover your data and resume operations, preventing costly downtime.
With cloud backup, you can create duplicate copies of important files and databases, ensuring that even if one location is affected by a disaster or failure, your data remains safe on remote servers.
This secondary off-site storage not only protects against data loss but also provides peace of mind knowing that your critical information is secure and can be easily restored when needed.
Remember to always assess and plan for potential disasters to tailor your disaster recovery strategies effectively. Stay informed about different types of disasters such as system failures, cyber-attacks, natural calamities like floods or fires as well as human errors so that you can determine the best approach for protecting your data with cloud backup solutions.
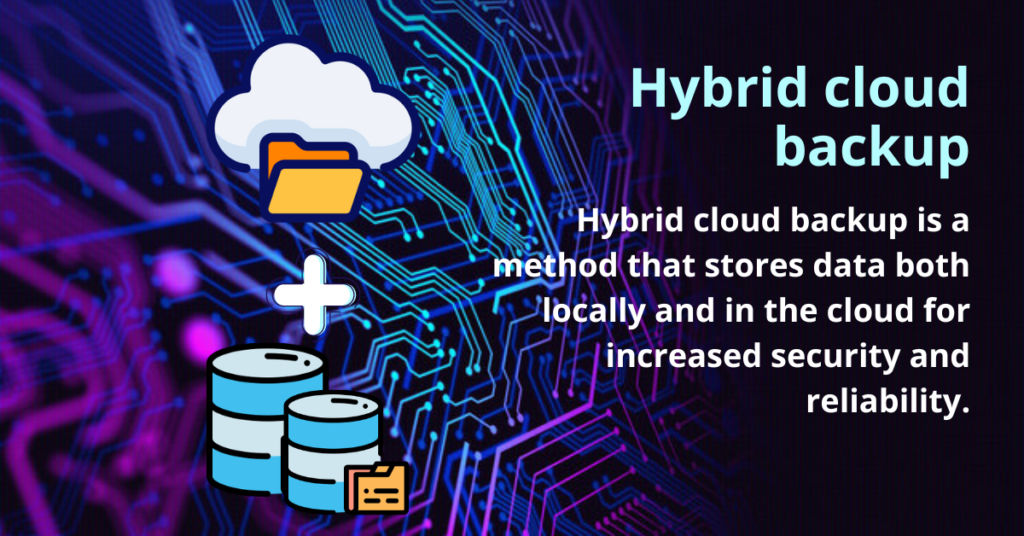
Hybrid cloud backup
Moving from disaster recovery strategies to other data storage types, let’s discuss the significance of a hybrid approach in safeguarding your data. Hybrid cloud backup involves utilizing a combination of public and private cloud solutions along with on-premises infrastructure to ensure comprehensive protection for your critical information.
This approach allows you to optimize cost-effectiveness while maintaining flexibility and control over sensitive data.
Hybrid cloud backup provides an extra layer of security by offering the advantages of both private and public clouds. It allows you to keep highly sensitive data within a secure on-premises environment while leveraging the scalability and accessibility of the public cloud for less critical information.
By incorporating this strategy, businesses can address various operational needs more effectively, ensuring data availability and integrity across diverse platforms.
Choosing the Right Cloud Backup Approach
Choose the most suitable cloud backup method by understanding different types and best practices. Tailor your data restoration plan to ensure efficient recovery.
Different types of cloud backup (incremental, differential, full)
Cloud backup offers different types of methods to ensure your data is safely stored and easily recoverable. Here are the main approaches:
- Incremental Backup:
- This type focuses on backing up only the data that has changed since the last backup.
- It reduces storage space and speeds up the backup process.
- Example: If you backed up a file on Monday, it will only back up changes made to that file from Tuesday to Friday.
- Differential Backup:
- Unlike incremental backup, this method backs up all changes made since the last full backup.
- It takes longer to complete compared to incremental backups but requires less time for restoration.
- Example: If you backed up a file on Monday, it will back up all changes made to that file until the next full backup is performed.
- Full Backup:
- This approach involves backing up all selected files and folders every time it runs.
- It provides a comprehensive backup but requires more time and storage space.
- Example: Every selected file and folder is completely backed up each time this method runs.
Understanding these types will help you choose the best approach for your specific data backup needs.

Image by rawpixel.com on Freepik
Best practices for data restoration
You must follow best practices for data restoration to ensure efficient recovery and minimal downtime. Here’s what you need to do:
- Regular Testing: Regularly test your data restoration processes to verify that backups are functioning correctly and can be restored without errors.
- Document Recovery Procedures: Document step-by-step procedures for restoring different types of data, including required tools and configurations.
- Data Integrity Checks: Perform regular data integrity checks on backup files to identify and address any corruption or missing data.
- Version Control: Implement version control mechanisms to manage multiple versions of backed-up data and ensure the ability to restore specific points in time.
- Consider Automation: Explore automation tools to streamline the data restoration process and reduce manual intervention.
Implementing these best practices ensures that your data restoration process is robust, reliable, and capable of minimizing disruptions in case of a disaster.
Special considerations for determining backup frequency
When determining backup frequency, consider the importance of your data. Assess how often it changes and its criticality for operations and decision-making. You should also factor in regulatory requirements or industry standards that dictate specific backup frequencies based on compliance needs.
For example, healthcare organizations may need more frequent backups to comply with HIPAA regulations.
Evaluate the impact of potential data loss on your business operations and customer trust. Consider backing up frequently if data loss could result in significant financial losses or reputational damage.
Additionally, assess the cost implications of different backup frequencies to find a balance between protection and affordability.
Finally, take into account technological advancements and best practices that recommend adjusting backup frequencies as your business grows or experiences changes in data usage patterns.
By staying informed about emerging trends and recommendations, you can ensure that your backup strategy aligns with current industry standards and best practices for optimal protection.
In conclusion, special considerations for determining backup frequency include assessing data importance, regulatory requirements, impact of potential loss on business operations and finances, cost implications, as well as staying informed about technological advancements and best practices to adjust accordingly.

Image by vectorjuice on Freepik
Security and Cost Considerations
Ensuring data security in the cloud is vital for protecting sensitive information, while evaluating the cost of cloud backup services helps in making informed decisions for your budget.
Ensuring data security in the cloud
When it comes to data security in the cloud, it’s important to safeguard your information from unauthorized access or breaches. You can do this by ensuring that the cloud backup service you choose has robust encryption measures in place for data protection.
Encrypted data is converted into a code that can only be deciphered with the right decryption key, effectively securing your files from prying eyes and cyber threats.
Furthermore, opting for a reputable cloud backup provider offering multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security. Multi-factor authentication requires users to provide two or more forms of verification before gaining access to their accounts, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized entry.
By implementing these advanced security features and choosing a reliable provider, you can protect your valuable data from potential security vulnerabilities and mitigate the risk of data breaches while using cloud backup services.
Evaluating cost of cloud backup services
When considering the cost of cloud backup services, it’s essential to weigh the expenses against potential data loss and downtime. Cloud backup can be more cost-effective than traditional methods because you only pay for the storage space you use, with no upfront hardware costs.
Additionally, cloud backup eliminates the need for physical storage devices and ensures that your data is secure in offsite locations. By using cloud backup, businesses save on infrastructure and maintenance costs while ensuring quick recovery in case of a disaster.
Understanding the pricing models offered by different cloud backup providers is crucial. Some providers charge based on storage volume, while others have tiered pricing that includes additional features such as enhanced security or faster data retrieval options at higher price points.
Comparing these factors will help you make an informed decision when evaluating the cost of cloud backup services to find a solution that best fits your budget and requirements for data protection.
Comparing cloud backup vs. local backup
What is Cloud Backup and its types?
Choosing between cloud backup and local backup can feel like deciding between two great ice cream flavors. Both have their perks! But, depending on what’s more important to you—security, accessibility, or cost— you might find one suits your needs better. Here’s a friendly comparison to help you understand the differences:
| Aspect | Cloud Backup | Local Backup |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Stores copies of files on remote servers provided by a third party. | Stores data on physical devices, like external hard drives, at your location. |
| Accessibility | Access data anywhere, anytime, with an internet connection. | Access is limited to the physical location of the backup device. |
| Disaster Recovery | Excellent for recovery; data is safe in a different location. | Riskier; if disaster strikes your location, backups could be lost too. |
| Cost | Subscription-based; can be cost-effective with scalable options. | One-time cost for physical storage devices, but may require replacements over time. |
| Security | Strong security measures in place, but relies on third-party protocols. | Complete control over security, but requires personal management of encryption and protection. |
| Scalability | Easy to increase storage space without physical limitations. | Limited by physical device capacity; requires purchasing additional hardware for more space. |
Cloud backup shines in disaster recovery and accessibility. It protects against data loss, ensuring you can recover quickly if something goes wrong. You’re also free to access your data wherever there’s internet. Local backup, on the other hand, gives you total control over your security and doesn’t depend on an internet connection. But, it can be vulnerable if a disaster hits your location.
Remember, your choice depends on what matters most to you. Whether it’s the ease of grabbing your data on the go or having full control over its security, there’s a perfect option out there for you.

Conclusion – What is Cloud Backup?
Congratulations!
You know what is cloud backup! With its cost-effectiveness, accessibility, and data security, it underpins the protection of your important files and enables swift recovery in times of need. This is very important with more and more people using the cloud to store their important information.
Now you’re ready to use the power of cloud backup to ensure your data is safeguarded against unforeseen disasters while enjoying the convenience of anytime, anywhere access.
FAQs – What is Cloud Backup?
1. What is cloud backup, and why should I use it?
Cloud backup is a method of data loss prevention. It uses cloud computing to store your data in a secondary location, either physical or virtual database. This offsite storage can help protect your information if anything happens to the original source.
2. How does cloud backup work as an offsite storage solution?
Cloud backup works by copying your data from its primary location to a secondary one using the internet. The copied data resides in a secure, remote server, which could be accessed anytime you need it.
3. Does cloud backup guarantee total prevention of data loss?
While no system can offer 100% assurance against all forms of data loss, cloud backups significantly improve chances of recovery by storing copies at different locations away from the primary database.
4. Is there any difference between Cloud Backup and Cloud Storage?
Yes! While both involve storing information on remote servers via internet, Cloud Backup involves making exact copies for recovery purposes while Cloud Storage primarily focuses on sharing and accessing files across devices.