Do you want to know which Internet Protocol Is Used To Transmit Encrypted Data?
If you are worried about your online privacy and security, HTTPS is the protocol that steps in to keep your data safe. This blog will show you how HTTPS, along with SSL/TLS protocols, encrypts your information, making it tough for hackers to get their hands on.
Stay secure online, learn the Internet Protocol To Transmit Encrypted Data and… read on!
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways about Internet Protocols To Transmit Encrypted Data
- HTTPS is the internet protocol to transmit encrypted data on the internet, making your information safe.
- SSL and TLS are security protocols that turn data into a secret code. This keeps hackers from seeing your personal info.
- Encryption changes data into cipher text, using keys to lock and unlock information. This protects your online activities.
- Secure communication protocols like HTTPS protect against cyber threats and ensure privacy when browsing or sharing online.
- Other secure internet protocols include FTP for moving files safely and DNS for connecting website names with addresses securely. This is important for long-term data storage.
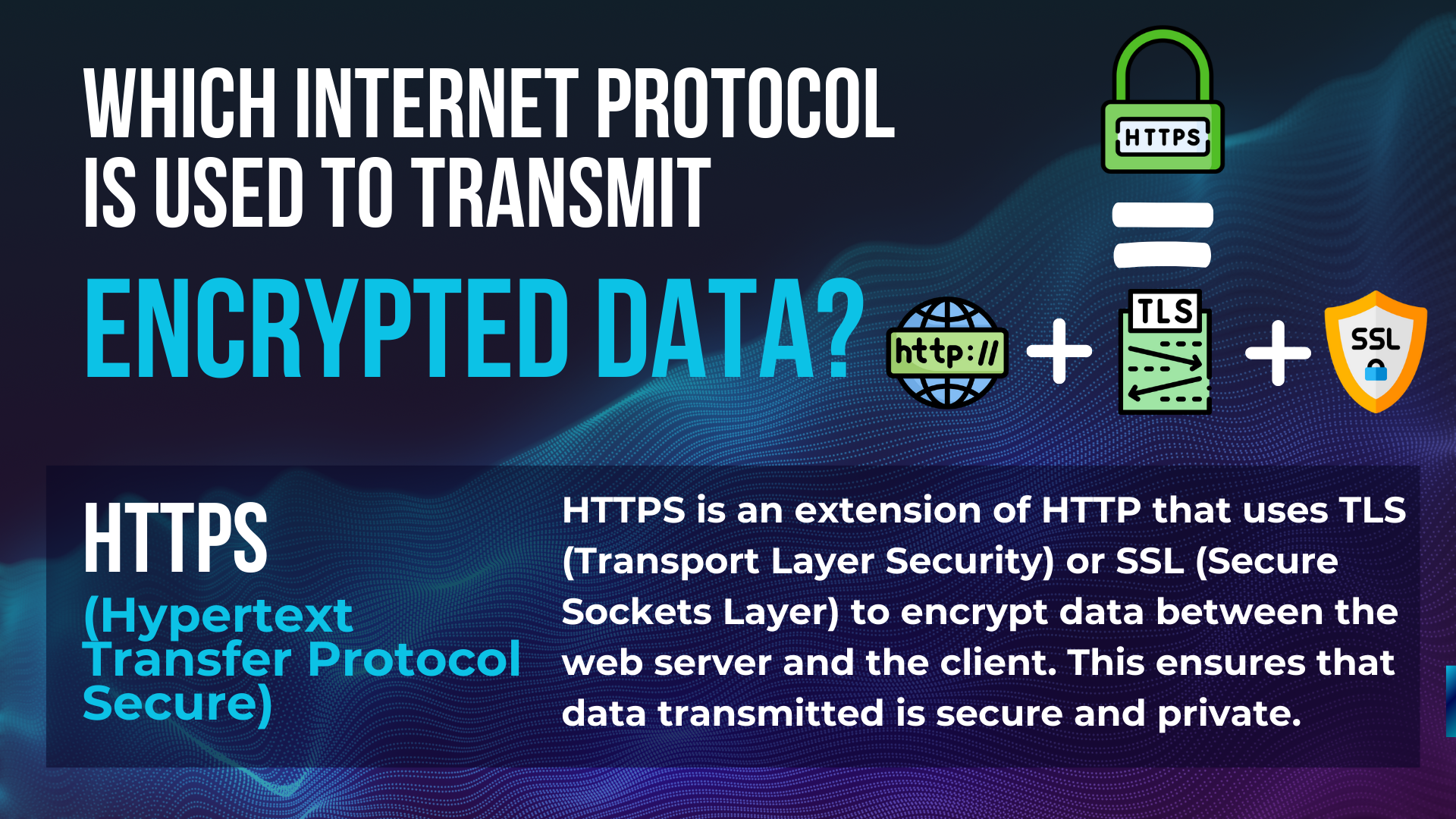
Which Internet Protocol Is Used To Transmit Encrypted Data?
HTTPS is the internet protocol that sends encrypted data. This means when you use a website with HTTPS in front, your information is safe. It uses Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS).
These make sure there’s a secure link between your web browser and the site’s server. SSL and TLS mix different encryption types to keep data hidden from others.
Now, understanding encryption helps see why HTTPS matters so much for online safety.
What is Encryption, and Why is it Important?
Encryption turns your info into a secret code. This keeps your data safe from hackers and prying eyes, making sure only those who should see it can. It is important to note that encryption is not the same as masking data.
You can learn about Static Vs Dynamic Data Masking on this blog post. If you are also interested to keep your data storage safe, like your cloud storage safety, you should check our guide on the best safety practices for cloud storage.
Definition of encryption
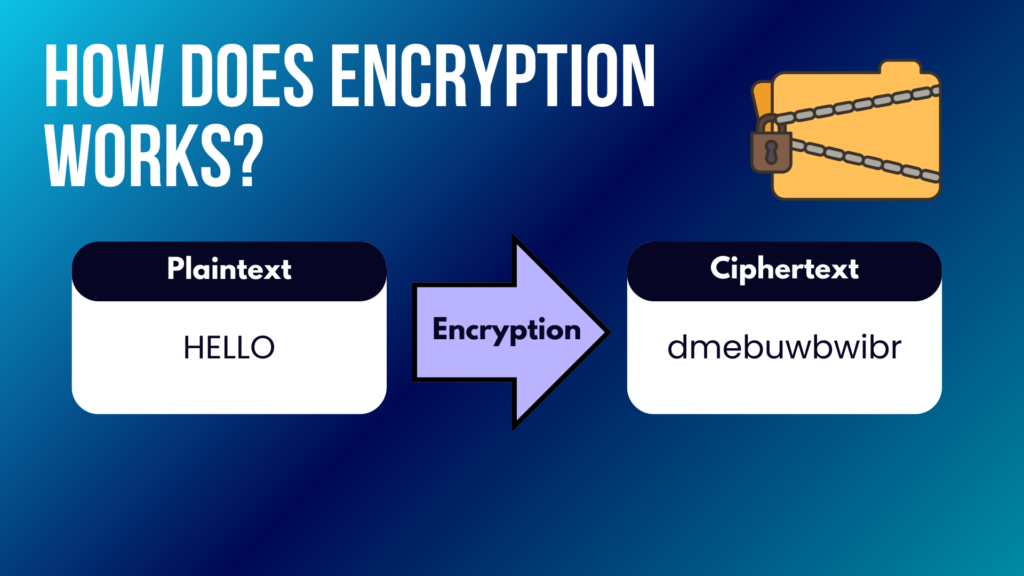
Encryption changes data into cipher text. This process keeps your information safe from people who should not see it. Two types of encryption are there: symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric encryption uses one secret key for both locking (encrypting) and unlocking (decrypting) information.
Asymmetric encryption, on the other hand, needs two keys – a public one to encrypt data and a private one to decrypt it. This method ensures that even if someone gets your encrypted data, they cannot read it without the correct key.

For instance, when you send an email or visit a website using HTTPS protocol, your data gets scrambled using these methods. Only the intended receiver can make sense of this scrambled message because they have the right key to decode it.
So even you’re shopping online, sending emails, or just browsing, encryption protects what you share over the internet keeping prying eyes out.
I think that, together with Internet Protocol To Transmit Encrypted Data, they keep your data safe and sound.
Importance of protecting sensitive data
Understanding encryption leads directly to the critical importance of protecting sensitive data. Every time you share personal information online, such as credit card numbers or login credentials, you risk hackers intercepting this information.
By encrypting this data, it turns into cipher text. This makes it unreadable to anyone who doesn’t have the key. Think about full disk encryption as a top method for keeping your laptop’s data safe if it gets lost or stolen.
In a world where data storage breaches are all too common, encrypting sensitive information is not just optional; it’s essential.
For secure encrypted data transmission on the internet, protocols like HTTPS and SSL/TLS play vital roles in safeguarding our personal details from cyberattacks. They ensure that only authorized parties can decrypt and view such sensitive information.
So every time you see “https://” in your web browser’s address bar before entering your details—you’re using one of these secure communication protocols to protect your privacy and security online.
In my experience, you should avoid opening HTTP links, because they are more likely to lead to unsafe sites.
Common Internet Protocols Used for Encrypted Data Transmission
Some key features make sure your data stays out of the wrong hands. HTTPS and SSL/TLS are like secret codes that keep your conversations private.
HTTPS
HTTPS makes sure your data is safe when you buy online or bank through the internet. Websites use it to keep your information secret from others. Think of HTTPS as a secure way to send letters where only you and the person getting it can read what’s inside.
This happens because of SSL and TLS, which are like secret codes that only your computer and the website understand.
Using HTTPS is crucial for any site dealing with private details. It changes data into a code while moving from a webpage to a server. This means hackers can’t see your credit card numbers or passwords when you enter them online.
Next, let’s talk about how SSL/TLS adds another layer of protection in this process.
SSL/TLS
SSL and TLS stand for Secure Sockets Layer and Transport Layer Security, respectively. These protocols make your internet use safe. They work like a secret handshake between your web browser and servers on the internet.
This secret handshake ensures that the data you send and receive is scrambled, keeping it private from anyone who might want to peek in.
SSL/TLS turns your data invisible to prying eyes while it travels across the internet.
These protocols keep your information hidden and also check if the server you’re connecting to is legitimate. Thanks to newer versions of SSL and TLS, this process has become even more secure with stronger encryption methods.
So when you see HTTPS instead of just HTTP in a website’s address, know that SSL or TLS is protecting your connection by wrapping your data in a secure layer before sending it out into the vast network.
How Does Encryption Work?
Encryption turns your data into a secret code before sending it over the internet. To do this, it uses special keys during what’s called a “key exchange” process—kind of like giving someone a private decoder ring to read your messages.
Key exchange
In key exchange, two sides share secret keys without anyone else knowing. This happens through asymmetric encryption. Your computer sends a public key to the website server. The server uses this public key to encrypt data and send it back.
Only your private key can unlock this data, making it readable just for you. Think of it as a secure handshake over the internet, where only you and the server know what’s being said.
This method ensures secure internet communication, especially during encrypted data transmission protocols like SSL/TLS handshakes. Each time you log into a website securely or send sensitive information online, this process kicks in to protect your data from prying eyes.
It’s like passing notes in class that only you and your friend can read—even if someone intercepts them, they won’t understand a thing.
Encrypted data transmission
SSL and TLS protocols mix two types of encryption to send your data safely. First, they use asymmetric encryption to swap keys without letting others see them. This step sets up a secure channel.
Then, they switch to symmetric encryption for the actual data sending because it’s faster. This way combines security with speed.
Every time you visit a secure website, these protocols work hard in the background. They keep your details safe from prying eyes during transit over the internet. Think of them as secret handshakes that only your computer and the website understand.
Encryption is like locking your valuables in a safe where only you know the combination.
Now, let’s look at why keeping our online conversations private matters so much.
The Importance of a Secure Communication Internet Protocol To Transmit Encrypted Data
Secure communication protocols keep hackers away and your secrets safe. They make sure no one can sneak a peek at your private chats or steal your personal info.
Protecting against cyberattacks
Cyberattacks threaten your online safety. Strong encryption methods, like WPA2 for Wi-Fi, block unwanted access to your data. Web traffic encryption with HTTPS and SSL/TLS protocols also shields information from hackers.
They scramble the data you send over the internet into a code that only the intended receiver can understand.
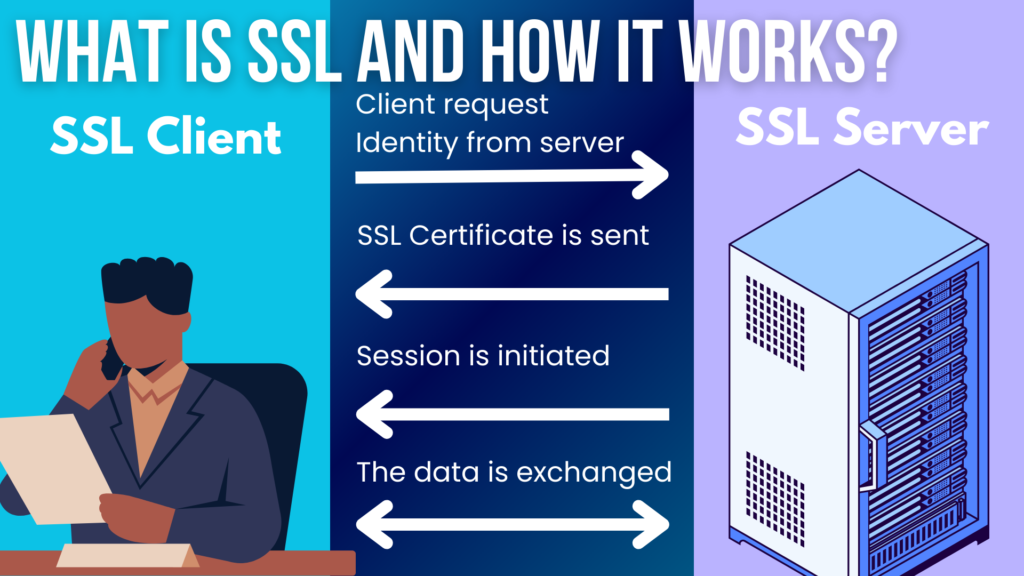
Using secure web communication tools ensures privacy and security. For example, when you log into a website, SSL certificates create a secure connection between your browser and the site’s server.
This stops others from seeing or stealing your information. Always look for “HTTPS” in the web address—it means your data is encrypted and safer from cyber threats.
Ensuring privacy and security in Internet Protocol To Transmit Encrypted Data
Securing your data online means using robust encryption technologies. SSL and TLS protocols play a key role here, making sure no one else can see or steal your information as it moves across the internet.
These secure data transmission methods turn your sensitive details into code that only the intended receiver can understand.
For emails on your mobile device, S/MIME protocol steps in to add another layer of protection, ensuring messages stay encrypted. If you’re working away from the office, setting up a VPN on your device is critical.
It creates a safe path for connecting back to company networks, guarding against unwanted eyes and cyber threats. This way, every piece of data shared over the web remains shielded from attackers aiming to compromise privacy and security standards.

Other Encrypted Internet Protocols To Transmit Encrypted Data
Beyond HTTPS and SSL/TLS, there’s a whole world of internet protocols to transmit encrypted data. These include FTP for secure file moves and DNS to connect website names with their Internet addresses—all fortressed against prying eyes.
SSL
Moving from TLS, let’s talk about SSL. SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer. It’s a protocol that makes sure the connection between your web browser and the server is secure. This means when you’re sending an email or checking a website, no one else can sneakily see what you’re doing.
It uses encryption to do this—kind of like translating your online activities into a secret code that only the website you’re visiting can understand.
SSL is crucial because it protects sensitive information from hackers. When you log into a website or send an email from your phone, SSL keeps your details safe. So, every time you see “https” in your browser’s address bar, it means SSL is at work keeping your data protected.
SSL turns browsing and emailing into secret missions where only you and the server know what’s being said.
TLS
TLS stands for Transport Layer Security. It’s the guard of internet communication, making sure data gets from point A to B safely. This protocol makes your web browsing safe. Think about when you log into your bank account or shop online; TLS is at work there.
It replaced SSL, its older cousin, bringing better security to the table.
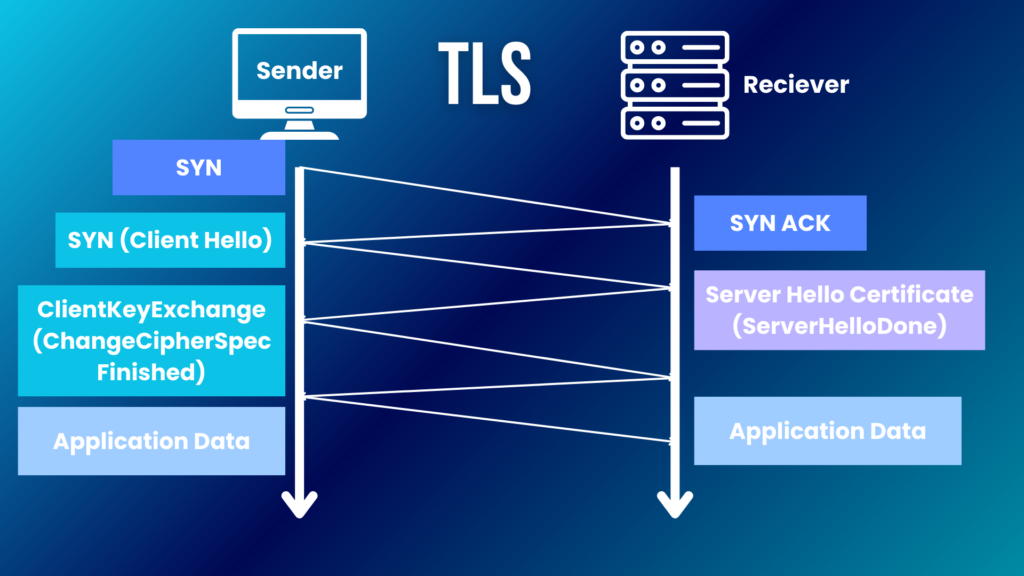
What happens is simple yet powerful—before your data starts moving across the internet, TLS and the website you’re visiting agree on a secret key. Only they know this key, which scrambles your information so no one else can read it while it travels.
When the data arrives where it needs to go, the website uses its key to unscramble the information and read it safely. This way, whether you’re sending emails or buying something with a credit card online, only you and the receiver can understand what’s being sent.
FTP
SSL sets the stage for secure data exchange, leading us to another key player in the internet protocol scene: FTP. This stands for File Transfer Protocol. It’s how files move across the internet.
Yet, unlike its counterparts SSL and TLS, FTP doesn’t directly deal with encrypted data transmission by default. For that extra layer of security, there’s a version known as Secure FTP or SFTP.
This secure path ensures your files travel safely over the web.
By using SFTP, you’re not just sending files; you’re wrapping them in a protective layer. Think of it like sealing a letter in an envelope before mailing it out. Secure file transfer is crucial when handling sensitive information—whether that’s personal data or confidential business documents.
With cyber threats lurking around every corner, choosing protocols like SFTP becomes more than just an option; it’s a necessity for protecting your digital footprint online.
DNS
After talking about FTP, we move to DNS. DNS stands for Domain Name System. This system turns website names you know into numbers the internet uses to find pages. Think of it as your phone’s contact list; instead of remembering everyone’s number, you just need their name.
DNS also has a secure version called DNSSEC. It protects the information sent between your device and websites. With this, no one can trick you into visiting a fake site that looks like a real one.
When using internet services like web browsers or Cloudflare, DNS ensures you get where you want to go safely.
Conclusion – Internet Protocol To Transmit Encrypted Data
HTTPS secures your online data. It uses SSL and TLS for a safe web journey. These protocols guard against spies. They check each website’s ID before sharing secrets. This keeps your info away from bad actors.
Banks, shops, and any site with private data rely on this tech. Without it, personal details could easily fall into the wrong hands.
SSL and TLS are now must-haves for safety-conscious web places. Sites need up-to-date certificates to keep your visits secure. Newer SSL/TLS versions bring tougher protection measures, making sure that every click you make is as safe as possible.
Together with the 3 2 1 backup storage rule, I consider that this makes your information really safeguarded.
Every time you see HTTPS in the address bar, you’re in a protected space where your data travels under heavy guard thanks to these encryption champions.

FAQs – Which Internet Protocol Is Used To Transmit Encrypted Data
Find out which internet protocol is used to transmit encrypted data.
1. What internet protocol secures your data as it travels?
HTTPS, with TLS encryption, guards your online info. Think of HTTPS as the secure version of HTTP, using TLS (the successor to SSL) to encrypt data in transit.
2. How does SSL work to protect web traffic?
SSL creates a secure channel over the internet… This means when you log into a website, SSL keeps hackers away by encrypting that connection between your browser and the server.
3. Can encrypted data be sent over Wi-Fi?
Yes! With wireless encryption methods like WPA2 or WPA3, your Wi-Fi network becomes a fortress. These protocols scramble data, so only intended recipients can read it.
4. Why is TLS preferred over SSL for securing websites?
TLS is newer and stronger than SSL… It uses robust encryption techniques to ensure that any data transferred between web servers and browsers remains private and intact.
5. Is there a difference between encrypted internet traffic and encrypted data transfer?
Not really; both terms deal with protecting information as it moves across the net or from one device to another—ensuring privacy and preventing unauthorized access.
6. How do public key infrastructures support secure communication?
Public key infrastructures manage keys for secure electronic transfers… They use asymmetric public key cryptography—meaning two keys are involved: one public for encrypting messages and one private for decrypting them, making sure only you can access what’s yours.