Welcome to our RAID Calculator, the go-to tool for quickly optimizing your data storage setup. With our RAID Calculator, you can effortlessly determine the best RAID level for your needs.
Simply select your preferred RAID level from our dropdown menu, input the number of drives and RAID groups, specify drive capacity and cost, and hit “Calculate” to instantly generate detailed metrics.
The RAID Calculator provides insights into usable space, data protection, fault tolerance, and more, all presented in easy-to-understand charts. Discover the power of RAID Calculators today and streamline your storage strategy like never before!
RAID Calculator
RAID Storage Calculator
Understanding RAID: What is RAID and How It Works
Are you frustrated by slow data access or worried about losing important files?
Use this simple, yet powerful RAID Calculator.
RAID, which stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks, offers a solution to these issues. This blog will guide you through understanding how RAID enhances data security and improves system performance by combining multiple disk units into one efficient storage solution.
Discover the key to unlocking improved data management—keep reading!
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks, combining multiple disk drives to boost performance and increase data safety.
- Different RAID levels like RAID 0, RAID 1, and RAID 5 offer unique balances between speeding up access to your files and protecting your data if a drive fails.
- Using RAID can protect important information from loss by storing copies in several places across different disks. This also allows computers to work faster when opening or saving files.

What is RAID, and How Does It Work?
What is RAID? It’s a data storage technology that uses multiple disk drives to enhance performance and provide fault tolerance.
How does it work? It distributes or replicates data across the array of drives, achieving a better speed and redundancy.
Meaning of RAID
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. This system saves the same data in different places on several hard drives or solid-state drives. By doing this, RAID joins multiple physical drives into a single unit.
This process boosts redundancy and amps up the performance and reliability of storage.
Different RAID levels, like RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 4, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10 each have unique features and purposes. For instance, while RAID 0 improves performance through data striping across disks, RAID 1 offers data mirroring for extra safety in case a drive fails.
Advanced levels such as RAID 5 and RAID 6 add parity blocks for error checking and data recovery, making sure your information stays safe even if something goes wrong with one of the disks.
And with something like RAID 10 you get both speed from striping and safety from mirroring all wrapped into one package.
These technologies are key to managing storage solutions effectively if you’re dealing with personal projects or large enterprise systems where losing data is not an option.
Types of RAID
Understanding RAID and its different configurations will help you make informed decisions about your storage needs and data management. Now, let’s delve into the types of RAID:
- RAID 0: Utilizes data striping across multiple disks for enhanced performance without redundancy.
- RAID 1: Involves mirroring data on two separate drives to provide redundancy in case of drive failure.
- RAID 4: Uses a dedicated parity drive to store error-checking information, allowing for data recovery in case of drive failure.
- RAID 5: Similar to RAID 4 but distributes the parity information across all drives for improved performance.
- RAID 6: Provides greater fault tolerance with an additional parity block compared to RAID 5.
- RAID 10: Combines mirroring and striping of data across multiple drives for both redundancy and improved performance.
- RAID 60: Combines the features of RAID 6 (double distributed parity) with RAID 0 (striping across RAID 6 arrays) for enhanced data protection and performance.
Understanding these types will help you to make an informed decision about your storage needs and managing your data effectively. And this RAID Calculator will definitely help you.
Benefits of using RAID
Now that you understand the types and workings of RAID, let’s look at the benefits of using RAID systems.
Using RAID provides data redundancy, meaning your data is stored in multiple locations across different drives, ensuring that if one drive fails, your data remains safe and accessible.
Additionally, RAID improves storage performance by combining multiple drives into a single logical unit, allowing for faster read and write operations. With RAID’s virtual disk technology and input/output operations, you can experience enhanced storage configurations that optimize data protection and fault tolerance to enhance overall storage reliability.
In summary, using RAID offers significant benefits such as improved reliability through data redundancy and better performance with advanced storage configurations while ensuring robust data protection for your critical information.
How RAID Works
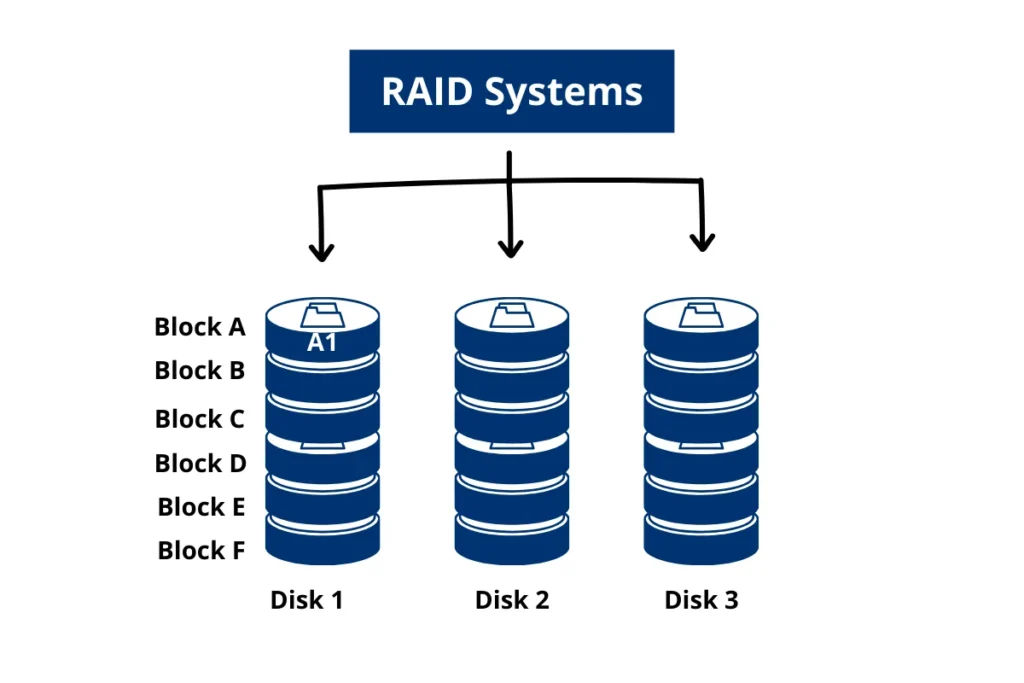
RAID works by distributing data across multiple disks (Data Striping) and creating duplicates of data (Data Redundancy). Virtual Disk Technology merges physical drives into a single logical unit for efficient Input/Output Operations.
Data Striping
RAID 0 uses data striping, where your data gets split into segments and stored across different drives. This boosts performance by allowing multiple disks to work together when reading or writing data.
Essentially, it’s like dividing a task among friends to get it done faster. The process of data striping is designed to enhance the speed of your storage system. Now let’s move on to explore the concept of Data Redundancy.
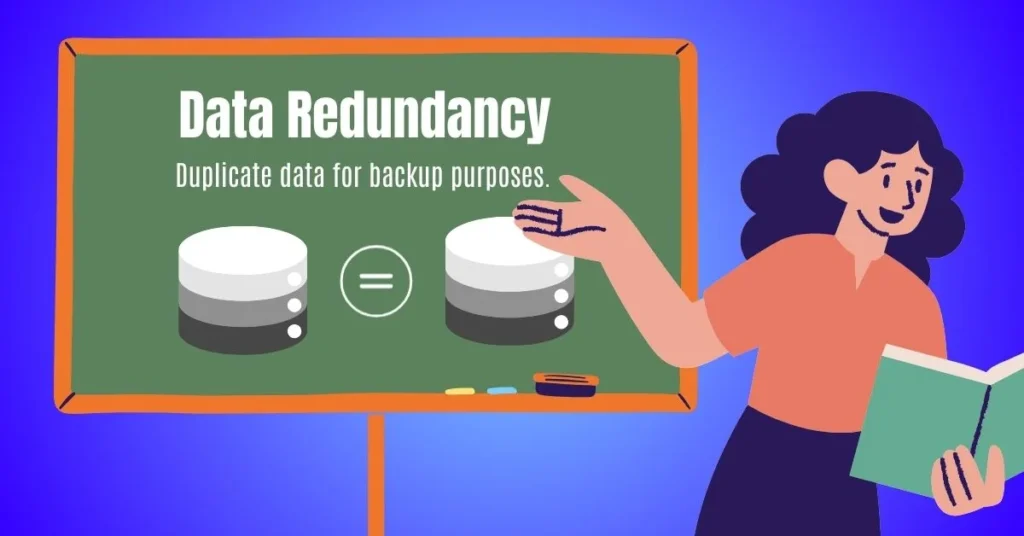
Data Redundancy
Data redundancy is a vital aspect of RAID. It involves storing the same data in multiple locations across different drives, ensuring that if one drive fails, the data remains accessible from other locations.
This redundancy provides an extra layer of security for your data, reducing the risk of loss or corruption due to hardware failures. By mirroring or striping data across multiple drives, RAID effectively safeguards your important information against potential disk malfunctions.
Understanding the significance of data redundancy within RAID can give you peace of mind when it comes to protecting your valuable files and documents. Whether it’s for personal use or within a business setting, having redundant copies of your data distributed across various drives ensures that even if one storage component fails, your information remains intact and readily available for use.
Virtual Disk Technology
Now, let’s talk about virtual disk technology. Virtual disk technology allows you to create a single storage unit from multiple physical drives, making it appear as one logical drive to the operating system.
This enhances performance and provides fault tolerance by distributing data across various disks while ensuring redundancy in case of drive failure. With this technology, you can efficiently manage and utilize your storage resources while safeguarding against potential data loss or system downtime.
Incorporating virtual disk technology into your storage infrastructure helps in improving data reliability and accessibility. It allows for seamless management of stored information and ensures that your systems operate smoothly under varying workloads or hardware failures.
Input/Output Operations
RAID involves Input/Output (I/O) operations, which refer to the processes of data being read from or written to storage devices. It enhances I/O performance by distributing tasks across multiple drives simultaneously, improving overall system speed and efficiency.
When a file is accessed, RAID can divide the I/O workload among several disks, enabling quicker retrieval of information. This means that when you’re working on projects or accessing files, the Input/Output operations are handled more efficiently due to RAID’s ability to balance and optimize data access across the storage drives.
In addition to optimizing performance through intelligent balancing of data transfer tasks between drives, it also improves fault tolerance – meaning your data remains accessible even if one drive fails.
By distributing I/O operations effectively and providing redundancy through mirroring or parity configurations, RAID ensures that your files remain accessible even in case of drive failure — providing an extra layer of security for your valuable digital assets.
RAID Levels and Configurations
RAID Levels and Configurations provide various options for optimizing data storage and security. They offer different ways to organize and protect your data. You can select your RAID type in our RAID Calculator
RAID 0
RAID 0 optimizes performance by splitting data across multiple drives for faster read and write speeds. However, it does not provide redundancy, meaning if one drive fails, all data is lost.
RAID 0 requires a minimum of two drives and delivers improved speed through simultaneous access to data on every drive. This setup combines the storage capacity of all drives into a single virtual disk, enhancing system performance for tasks like video editing and gaming.
In real-life terms, imagine your favorite video game loading much faster because RAID 0 distributes the game files across multiple drives to boost access speed. However, if one drive fails, you could lose all your game progress stored in that array!
RAID 1
RAID 1 involves mirroring data on two separate drives, providing redundancy in case of drive failure. It means that everything written to one disk is simultaneously written to another disk.
This setup ensures that if one drive fails, the other drive still has all the information intact. Essentially, RAID 1 offers a simple and effective way to safeguard your data against hardware malfunctions.
In RAID 1 configuration, both disks hold identical copies of the same data. So if one disk were to fail, you can continue using the system and retrieve your lost data from the remaining working disk without any interruptions or delays.
This level of fault tolerance provides peace of mind, especially for businesses where uninterrupted access to critical information is paramount.

RAID 5
RAID 5 combines data striping and parity to provide fault tolerance and data protection. It requires a minimum of three drives, with data striped across all the disks along with parity information for error-checking purposes.
If one drive fails, the system can rebuild the lost data using the remaining drives and parity information. This level provides a good balance between performance, storage capacity, and data redundancy, making it suitable for many business environments seeking improved reliability.
In RAID 5, each write request involves updating both data and parity information distributed across all the drives in the array, ensuring redundancy in case of drive failure. With its ability to continue functioning even if one drive fails, RAID 5 offers enhanced fault tolerance compared to other levels like RAID 0 or RAID 1.
The distribution of parity across multiple disks also contributes to efficient use of storage space while maintaining high performance levels.
RAID 10
RAID 10 combines the features of RAID 1 and RAID 0. It provides both redundancy and improved performance by mirroring and striping data across multiple drives. This configuration offers high fault tolerance as well as excellent read/write speeds, making it ideal for applications where both performance and data protection are crucial.
Moving on to “Data Security and Recovery with RAID”, let’s dive deeper into ensuring the safety of your valuable information.
RAID 60
RAID 60 is a type of data storage setup that combines two RAID levels: RAID 6 and RAID 0.
In RAID 60, data is organized across multiple hard drives in a way that offers both data protection and performance benefits. It works by striping data (RAID 0) across multiple RAID 6 arrays. RAID 6 itself provides redundancy by using two parity blocks across the drives, which means it can tolerate the failure of up to two drives without losing data. By combining multiple RAID 6 arrays in a RAID 0 configuration, RAID 60 enhances performance through striping while maintaining strong data protection capabilities.
This makes RAID 60 suitable for applications that require high data availability and performance, such as large-scale databases and data-intensive servers.
Data Security and Recovery with RAID
Ensure your data is secure and recoverable by understanding RAID. Learn more about this crucial topic to safeguard your information effectively.
Fault Tolerance
Fault tolerance is a crucial aspect of RAID, ensuring that your data remains accessible even if one or more drives fail. With RAID 1, for example, the mirrored setup allows the system to continue operating without any loss of data when a drive fails.
In RAID 5 and RAID 6, dedicated parity blocks enable the storage system to reconstruct lost data when a drive fails by using error-checking information. These fault-tolerant capabilities make RAID an ideal choice for safeguarding your important information.
Moving on to “Data Protection,” let’s delve into how RAID ensures the security of your valuable data.
Data Protection
When it comes to data protection, RAID provides fault tolerance and redundancy by storing the same data in different locations on multiple drives. This means that if one drive fails, your data is still safe and accessible from other drives in the array.
With RAID 1, for example, your data is mirrored across two separate drives, ensuring that even if one drive fails, your information remains secure and available.
In addition to fault tolerance, RAID offers data protection through solutions like RAID recovery and storage configurations such as RAID 5 and RAID 6. These configurations use dedicated parity drives to store error-checking information, allowing for seamless data recovery in case of a drive failure.
Essentially, with different RAID levels and configurations at hand, you can rest assured that your valuable data is well-protected against potential hardware failures or errors.
RAID Recovery
When a disk in a RAID array fails, the data is still accessible because of redundancy. Each disk contains part of the data, so even if one fails, the information can be reconstructed using parity information or data mirroring from other disks.
This restores your data, ensuring that you don’t lose any important files.
Understanding RAID recovery ensures that you are prepared for unexpected failures and can maintain access to your valuable data. Moving on to “Storage Solutions,” let’s delve into how RAID is commonly used in enterprise environments to improve reliability and performance.
Storage Solutions
Now, let’s move from understanding how RAID helps with data recovery to discussing its storage solutions. In enterprise environments, RAID storage solutions are commonly used to improve data reliability and performance.
You can choose the best RAID level based on your specific needs, whether it’s for redundancy, improved performance, or a balance of both. Understanding the different configurations of RAID can help you make informed decisions about your storage needs and data management.
This ensures that your data is well-protected while maintaining efficient access.
In considering storage solutions, it’s essential to remember that the right one depends on balancing redundancy and performance according to your requirements. The RAID offers various levels suitable for diverse needs – from basic redundancy in RAID 1 to high-performance striping in RAID 0 or balanced approaches like those found in RAIDs 5 and 10.
Making an informed decision when choosing a storage solution will provide you with reliable access while safeguarding your valuable information.

Conclusion – RAID Calculator
Congratulations! You’ve now mastered the fundamentals of RAID technology. With a clear grasp of its benefits, various levels, and configurations, you’re ready to make informed decisions about your storage needs.
RAID’s ability to enhance data reliability and performance makes it an invaluable asset in enterprise environments. Your understanding of RAID opens up opportunities for seamless data management and improved storage solutions.
Keep exploring this dynamic field; there’s always more to uncover in the world of data storage.
FAQs
1. What is RAID?
RAID stands for a system that combines multiple disk arrays to store data more safely or quickly. It helps your computer perform better by improving how it does input/output operations.
2. How does RAID work?
RAID works by organizing your data across several disk arrays. This setup can either protect your information if a disk fails or make accessing data faster because it uses multiple disks for input/output operations at once.
3. Can RAID improve my computer’s performance?
Yes, RAID can significantly boost your computer’s performance, especially during input/output operations, making tasks like loading programs and files quicker.
4. Is setting up RAID right for me?
Setting up RAID might be a good choice if you need extra safety for your stored data or if you want to speed up how fast your computer performs input/output operations.


